Dyslipidemia in rheumatoid arthritis: the possible mechanisms
- PMID: 37954591
- PMCID: PMC10634280
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1254753
Dyslipidemia in rheumatoid arthritis: the possible mechanisms
Abstract
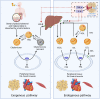
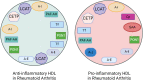
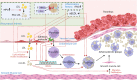
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune inflammatory disease, of which the leading cause of death is cardiovascular disease (CVD). The levels of total cholesterol (TC), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-c), and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-c) in RA decrease especially under hyperinflammatory conditions. It is conflictive with the increased risk of CVD in RA, which is called "lipid paradox". The systemic inflammation may explain this apparent contradiction. The increased systemic proinflammatory cytokines in RA mainly include interleukin-6(IL-6)、interleukin-1(IL-1)and tumor necrosis factor alpha(TNF-α). The inflammation of RA cause changes in the subcomponents and structure of HDL particles, leading to a weakened anti-atherosclerosis function and promoting LDL oxidation and plaque formation. Dysfunctional HDL can further worsen the abnormalities of LDL metabolism, increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease. However, the specific mechanisms underlying lipid changes in RA and increased CVD risk remain unclear. Therefore, this article comprehensively integrates the latest existing literature to describe the unique lipid profile of RA, explore the mechanisms of lipid changes, and investigate the impact of lipid changes on cardiovascular disease.
Keywords: cardiovascular disease; dyslipidemia; high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; mechanism; rheumatoid arthritis.
Copyright © 2023 Yan, Yang, Han, Ba, Shen, Lin, Li, Zhang, Huang, Huang, Qin, Wang, Tu and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Peters MJ, Symmons DP, Mccarey D, Dijkmans BA, Nicola P, Kvien TK, et al. . EULAR evidence-based recommendations for cardiovascular risk management in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other forms of inflammatory arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis (2010) 69:325–31. doi: 10.1136/ard.2009.113696 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

