Saudi Adults' Understanding and Views of Weight Management Practices and Obesity
- PMID: 37954890
- PMCID: PMC10637233
- DOI: 10.2147/DMSO.S433721
Saudi Adults' Understanding and Views of Weight Management Practices and Obesity
Abstract
Background and objective: The rising prevalence of overweight and obesity presents a significant global challenge. This study aimed to investigate the understanding and views of weight management practices and obesity among Saudi adults.
Methodology: A cross-sectional online survey was conducted from October 2022 to January 2023 among adults residing in Saudi Arabia. Participants completed a self-administered 41-item questionnaire designed to assess their understanding and views regarding weight management practices and obesity.
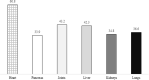
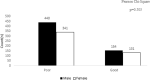
Results: A total of 1066 participants completed the survey. Gender distribution showed a majority of males (55.7%). Age-wise, the majority fell below 51 years, with 37.7% (young) between 18-24, 32.7% (young adult) between 25-33, and 21.3% (adult) between 34-51. Employment was reported by one-third (n = 315) of respondents, while 22.0% (n = 234) had a history of chronic diseases. Furthermore, 77.3% (n = 824) engaged in regular physical activity.The study results revealed that participants' mean score for understanding obesity was 3.28 ± 2.37 (range 0-6), while the average views score was 28.08 ± 8.79 (range 0-34). Furthermore, females displayed a higher level of understanding compared to males. Employment status also played a significant role, with employed individuals having a better understanding of obesity than those who were unemployed. Moreover, participants with higher qualifications demonstrated a more comprehensive understanding of obesity compared to those with lower qualifications. Additionally, individuals with higher monthly income levels displayed a greater understanding of obesity compared to those with lower incomes. Lastly, participants who engaged in regular physical activity exhibited a higher level of understanding compared to those who were physically inactive.
Conclusion: The study indicates that factors such as being older, being female, being employed, having higher education and income, and engaging in regular physical activity are associated with increased understanding and favorable views regarding weight management practices and obesity.
Keywords: Saudi Arabia; obesity; overweight; prevalence; weight management.
© 2023 Alshehri and Alorfi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Awareness of Obesity and Weight Loss Management Among Adults in the Asir Region, Saudi Arabia.Cureus. 2024 Dec 3;16(12):e75066. doi: 10.7759/cureus.75066. eCollection 2024 Dec. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39759738 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge and Attitude of the General Population in Saudi Arabia Toward Weight Management Medications (WMMs): A Cross-Sectional Study.Cureus. 2023 Aug 2;15(8):e42875. doi: 10.7759/cureus.42875. eCollection 2023 Aug. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37664345 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge, attitude, and practices toward dengue fever among the public: a cross-sectional study in the Western region of Saudi Arabia.Front Public Health. 2024 Mar 6;12:1327427. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1327427. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 38510353 Free PMC article.
-
High prevalence of overweight and obesity in Saudi Arabia.Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1996 Jun;20(6):547-52. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord. 1996. PMID: 8782731
-
Levels and correlates of physical activity, inactivity and body mass index among Saudi women working in office jobs in Riyadh city.BMC Womens Health. 2016 Jun 20;16:33. doi: 10.1186/s12905-016-0312-8. BMC Womens Health. 2016. PMID: 27323844 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Evaluation of clinical aspects of obesity among undergraduate healthcare students- a cross-sectional study at King Saud University, Riyadh, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.J Health Popul Nutr. 2024 Oct 14;43(1):159. doi: 10.1186/s41043-024-00651-y. J Health Popul Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39402641 Free PMC article.
-
Awareness of Obesity and Weight Loss Management Among Adults in the Asir Region, Saudi Arabia.Cureus. 2024 Dec 3;16(12):e75066. doi: 10.7759/cureus.75066. eCollection 2024 Dec. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39759738 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence and factors associated with weight loss medicine usage in the Hail population, Saudi Arabia.J Educ Health Promot. 2025 May 30;14:223. doi: 10.4103/jehp.jehp_24_25. eCollection 2025. J Educ Health Promot. 2025. PMID: 40575518 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Engin A. The definition and prevalence of obesity and metabolic syndrome. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017;960:1–17. - PubMed
-
- Alluhidan M, Alsukait RF, Alghaith T, et al. Overview: challenges and opportunities for obesity prevention in Saudi Arabia; 2022.
-
- Ritchie H, Roser M. Micronutrient Deficiency. Our World in data; 2017.
-
- World Health Organization. World Obesity Day 2022-Accelerating Action to Stop Obesity. World Health Organization; 2022.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

