The efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity of plague vaccines: A systematic literature review
- PMID: 37954941
- PMCID: PMC10637890
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crimmu.2023.100072
The efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity of plague vaccines: A systematic literature review
Abstract
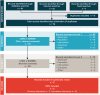
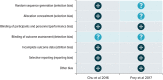
Plague remains endemic in many parts of the world, and despite efforts, no preventative vaccine is available. We performed a systemic review of available randomised controlled trials (RCTs) of live, attenuated, or killed plague vaccines vs. placebo, no intervention, or other plague vaccine to evaluate their efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity. Data sources included MEDLINE, Embase, and the Cochrane Library; clinical trial registers; and reference lists of included studies. Primary outcomes were efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity. Risk of bias was assessed using the Cochrane Collaborations tool. Only 2 RCTs, both on subunit vaccines, were included out of the 75 screened articles. The 2 trials included 240 participants with a follow-up of 3 months and 60 participants with a follow-up of 13 months, respectively. Safety evidence was limited, but both vaccines were well tolerated, with only mild to moderate adverse events. Both vaccines were immunogenic in a dose-dependent manner. However, given the limited data identified in this systematic review, we are unable to quantify the efficacy of vaccines to prevent plague, as well as their long-term safety and immunogenicity. More trials of plague vaccines are needed to generate additional evidence of their long-term effects.
Keywords: Bubonic plague; Plague vaccine; Pneumonic plague; Yersinia pestis.
© 2023 RTI Health Solutions.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form at www.icmje.org/coi_disclosure.pdf. LH, SH, and EH have no financial relationships with any organisations that might have an interest in the submitted work in the previous three years; and no other relationships or activities to declare that could appear to have influenced the submitted work.
Figures
References
-
- Bertherat E. Plague around the world, 2010-2015. Wkly. Epidemiol. Rec. 2016;91(8):89–93. - PubMed
-
- Bertherat E. Plague around the world in 2019. Wkly. Epidemiol. Rec. 2019;94(25):289–292.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . 2018. Facts about Pneumonic Plague.https://emergency.cdc.gov/agent/plague/factsheet.asp
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources