The APOE-R136S mutation protects against APOE4-driven Tau pathology, neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation
- PMID: 37957317
- PMCID: PMC10689245
- DOI: 10.1038/s41593-023-01480-8
The APOE-R136S mutation protects against APOE4-driven Tau pathology, neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation
Abstract
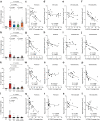
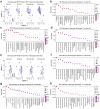
Apolipoprotein E4 (APOE4) is the strongest genetic risk factor for late-onset Alzheimer's disease (LOAD), leading to earlier age of clinical onset and exacerbating pathologies. There is a critical need to identify protective targets. Recently, a rare APOE variant, APOE3-R136S (Christchurch), was found to protect against early-onset AD in a PSEN1-E280A carrier. In this study, we sought to determine if the R136S mutation also protects against APOE4-driven effects in LOAD. We generated tauopathy mouse and human iPSC-derived neuron models carrying human APOE4 with the homozygous or heterozygous R136S mutation. We found that the homozygous R136S mutation rescued APOE4-driven Tau pathology, neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation. The heterozygous R136S mutation partially protected against APOE4-driven neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation but not Tau pathology. Single-nucleus RNA sequencing revealed that the APOE4-R136S mutation increased disease-protective and diminished disease-associated cell populations in a gene dose-dependent manner. Thus, the APOE-R136S mutation protects against APOE4-driven AD pathologies, providing a target for therapeutic development against AD.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Y. Huang and R.W.M. are involved in establishing and managing GABAeron, Inc. Q.X. works part time at GABAeron, Inc. J.F.A.-V. is a co-inventor on a patent application describing methods and compositions for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease via APOE Christchurch. Other authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
















References
-
- Koutsodendris N, Nelson MR, Rao A, Huang Y. Apolipoprotein E and Alzheimer’s disease: findings, hypotheses, and potential mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2022;17:73–99. - PubMed
-
- Harris FM, Brecht WJ, Xu Q, Mahley RW, Huang Y. Increased tau phosphorylation in apolipoprotein E4 transgenic mice is associated with activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase: modulation by zinc. J. Biol. Chem. 2004;279:44795–44801. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

