Association of Chondrolabral Lesions with Ultrasound-Guided Detection of Pathological Head-Neck Contour
- PMID: 37958230
- PMCID: PMC10649636
- DOI: 10.3390/diagnostics13213334
Association of Chondrolabral Lesions with Ultrasound-Guided Detection of Pathological Head-Neck Contour
Abstract
Objective: This study aimed to investigate whether the asphericity of the neck-head junction of the femur confirmed via ultrasound is associated with further pathology due to femoro-acetabular impingement (FAI).
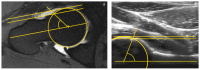
Methodology: After a clinical examination with positive FAI tests, an ultrasound examination of the hip was performed. In the case of asphericity, a quantitative ultrasound-assisted assessment of the hip was performed, followed by contrast-enhanced arthro-MRI with the question of cartilage or labral damage.
Results and conclusions: We included 51 patients with a mean age of 35.25. According to the examination algorithm, asphericity was present in all patients via ultrasonography. The average anterior alpha angle (AAA) determined in ultrasonography was 43.49°. The average AAA on the arthro-MRI was 44.19°. The mean anterior head neck offset (AHNO) in ultrasound was 5.27 mm, and in arthro-MRI, it was 5.36 mm. Arthro-MRI confirmed a bump in 47 patients and a talization disorder in 4 patients. In 49 patients, a labral lesion was found, with one being a re-rupture. Furthermore, in one patient, labral degeneration was identified. Cartilage damage to the hip joint was found in 25 patients. Two patients had neither labral nor cartilage damage in the arthro-MRI. In our study, sonographically confirmed asphericity of the head-neck junction was found in 49 cases, which was associated with further pathology and, according to the current doctrine, was attributable to the FAI and required surgical intervention. This study shows that the detection of a pathologic head and neck contour via ultrasound in combination with positive clinical signs, as present in FAI, is associated with chondrolabral lesions detected via arthro-MRI in 96.1% of cases.
Keywords: MRI; femoroacetabular impingement; impingement; ultrasound.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. None of the authors, their immediate family, or any research foundation with which they are affiliated received any financial payments or other benefits from any commercial entity related to the subject of this article.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

