Analysis of CD74 Occurrence in Oncogenic Fusion Proteins
- PMID: 37958963
- PMCID: PMC10650716
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms242115981
Analysis of CD74 Occurrence in Oncogenic Fusion Proteins
Abstract
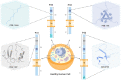
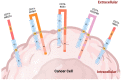
CD74 is a type II cell surface receptor found to be highly expressed in several hematological and solid cancers, due to its ability to activate pathways associated with tumor cell survival and proliferation. Over the past 16 years, CD74 has emerged as a commonly detected fusion partner in multiple oncogenic fusion proteins. Studies have found CD74 fusion proteins in a range of cancers, including lung adenocarcinoma, inflammatory breast cancer, and pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia. To date, there are five known CD74 fusion proteins, CD74-ROS1, CD74-NTRK1, CD74-NRG1, CD74-NRG2α, and CD74-PDGFRB, with a total of 16 different variants, each with unique genetic signatures. Importantly, the occurrence of CD74 in the formation of fusion proteins has not been well explored despite the fact that ROS1 and NRG1 families utilize CD74 as the primary partner for the formation of oncogenic fusions. Fusion proteins known to be oncogenic drivers, including those of CD74, are typically detected and targeted after standard chemotherapeutic plans fail and the disease relapses. The analysis reported herein provides insights into the early intervention of CD74 fusions and highlights the need for improved routine assessment methods so that targeted therapies can be applied while they are most effective.
Keywords: CD74-NRG1; CD74-NRG2α; CD74-NTRK1; CD74-PDGFRB; CD74-ROS1; cancer; cluster of differentiation 74 (CD74); fusion gene; oncogenic fusion protein.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Multidriver mutation analysis in pulmonary mucinous adenocarcinoma in Taiwan: identification of a rare CD74-NRG1 translocation case.Med Oncol. 2014 Jul;31(7):34. doi: 10.1007/s12032-014-0034-4. Epub 2014 Jun 10. Med Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24913807
-
Differential Subcellular Localization Regulates Oncogenic Signaling by ROS1 Kinase Fusion Proteins.Cancer Res. 2019 Feb 1;79(3):546-556. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-1492. Epub 2018 Dec 11. Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30538120 Free PMC article.
-
A case of lung adenocarcinoma with a novel CD74-ROS1 fusion variant identified by comprehensive genomic profiling that responded to crizotinib and entrectinib.Thorac Cancer. 2021 Sep;12(18):2504-2507. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.14093. Epub 2021 Jul 28. Thorac Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34319660 Free PMC article.
-
ROS1 protein-tyrosine kinase inhibitors in the treatment of ROS1 fusion protein-driven non-small cell lung cancers.Pharmacol Res. 2017 Jul;121:202-212. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2017.04.022. Epub 2017 Apr 30. Pharmacol Res. 2017. PMID: 28465216 Review.
-
Brain Metastases in Lung Cancers with Emerging Targetable Fusion Drivers.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Feb 19;21(4):1416. doi: 10.3390/ijms21041416. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32093103 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive identification of NRG1 fusions in 25,203 patients with solid tumors.NPJ Precis Oncol. 2025 Jul 29;9(1):262. doi: 10.1038/s41698-025-01044-y. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40730881 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive genomic characterization of hematologic malignancies at a pediatric tertiary care center.Front Oncol. 2024 Dec 2;14:1498409. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1498409. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39687881 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals Early Alterations Associated with Intrinsic Resistance to Targeted Therapy in Lung Adenocarcinoma Cell Lines.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jul 8;16(13):2490. doi: 10.3390/cancers16132490. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39001552 Free PMC article.
-
Insight into NSCLC through novel analysis of gene interactions and characteristics.Am J Clin Exp Immunol. 2024 Apr 25;13(2):58-67. doi: 10.62347/ANLV4963. eCollection 2024. Am J Clin Exp Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38765019 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Giménez-Capitán A., Sánchez-Herrero E., Robado de Lope L., Aguilar-Hernández A., Sullivan I., Calvo V., Moya-Horno I., Viteri S., Cabrera C., Aguado C., et al. Detecting ALK, ROS1 and RET fusions and the METΔex14 splicing variant in liquid biopsies of non-small cell lung cancer patients using RNA-based techniques. Mol. Oncol. 2023;17:1884–1897. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.13468. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

