Radiologic Progression of Interstitial Lung Abnormalities following Surgical Resection in Patients with Lung Cancer
- PMID: 37959324
- PMCID: PMC10647667
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12216858
Radiologic Progression of Interstitial Lung Abnormalities following Surgical Resection in Patients with Lung Cancer
Abstract
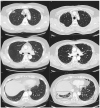
In this study, we aimed to assess the prevalence of interstitial lung abnormalities (ILAs) and investigate the rates and risk factors associated with radiologic ILA progression among patients with lung cancer following surgical resection. Patients who underwent surgical resection for lung cancer at our institution from January 2015 to December 2020 were retrospectively evaluated and grouped according to their ILA status as having no ILAs, equivocal ILAs, or ILAs. Progression was determined by simultaneously reviewing the baseline and corresponding follow-up computed tomography (CT) scans. Among 346 patients (median age: 67 (interquartile range: 60-74) years, 204 (59.0%) men), 22 (6.4%) had equivocal ILAs, and 33 (9.5%) had ILAs detected upon baseline CT. Notably, six patients (6/291; 2.1%) without ILAs upon baseline CT later developed ILAs, and 50% (11/22) of those with equivocal ILAs exhibited progression. Furthermore, 75.8% (25/33) of patients with ILAs upon baseline CT exhibited ILA progression (76.9% and 71.4% with fibrotic and non-fibrotic ILAs, respectively). Multivariate analysis revealed that ILA status was a significant risk factor for ILA progression. ILAs and equivocal ILAs were associated with radiologic ILA progression after surgical resection in patients with lung cancer. Hence, early ILA detection can significantly affect clinical outcomes.
Keywords: computed tomography; interstitial lung abnormalities; lung cancer; progression; surgical resection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Hatabu H., Hunninghake G.M., Richeldi L., Brown K.K., Wells A.U., Remy-Jardin M., Verschakelen J., Nicholson A.G., Beasley M.B., Christiani D.C., et al. Interstitial lung abnormalities detected incidentally on CT: A Position Paper from the Fleischner Society. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020;8:726–737. doi: 10.1016/S2213-2600(20)30168-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Araki T., Putman R.K., Hatabu H., Gao W., Dupuis J., Latourelle J.C., Nishino M., Zazueta O.E., Kurugol S., Ross J.C., et al. Development and progression of interstitial lung abnormalities in the Framingham heart study. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2016;194:1514–1522. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201512-2523OC. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

