Adsorption and Visible Photocatalytic Synergistic Removal of a Cationic Dye with the Composite Material BiVO4/MgAl-LDHs
- PMID: 37959476
- PMCID: PMC10650294
- DOI: 10.3390/ma16216879
Adsorption and Visible Photocatalytic Synergistic Removal of a Cationic Dye with the Composite Material BiVO4/MgAl-LDHs
Abstract
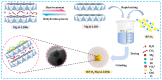
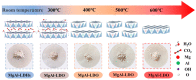
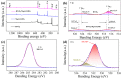
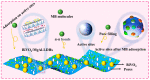
Adsorption and photocatalysis are effective in removing organic pollutants from wastewater. This study is based on the memory effects of MgAl-layered double hydroxides (MgAl-LDHs) after high-temperature calcination. By introducing bismuth vanadate (BiVO4) during the reformation of the layered structure via contact with water, a composite material BiVO4/MgAl-LDHs with enhanced adsorption and visible light catalytic performance was synthesized. The effects of the calcination temperature, ratio, initial methylene blue (MB) concentration, and catalyst dosage on the adsorption and photocatalytic performance were investigated. The BiVO4/MgAl-LDHs showed better photocatalytic performance than the pure BiVO4 and MgAl-LDHs. Under the optimal conditions, the proportion of MB adsorbed in 20 min was 66.1%, and the percentage of MB degraded during 100 min of photolysis was 92.4%. The composite photocatalyst showed good chemical stability and cyclability, and the adsorption-degradation rate was 86% after four cycles. Analyses of the adsorption and photocatalytic mechanisms for the composite material showed that synergistic adsorption and visible light photocatalysis contributed to the excellent catalytic performance of the BiVO4/MgAl-LDHs. A highly adsorbent photocatalytic composite material exhibiting outstanding performance was prepared via a simple, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly method, providing reference information for the removal of organic pollutants from liquids.
Keywords: BiVO4; MgAl–LDHs; adsorption-visible photocatalytic performance; memory effect; organic pollutants.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interest or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures









References
-
- Martínez-de La Cruz A., Pérez U.M.G. Photocatalytic properties of BiVO4 prepared by the co-precipitation method: Degradation of rhodamine B and possible reaction mechanisms under visible irradiation. Mater. Res. Bull. 2010;45:135–141. doi: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2009.09.029. - DOI
-
- Tao Y., Ni Q., Wei M., Xia D., Li X., Xu A. Metal-free activation of peroxymonosulfate by g-C3N4 under visible light irradiation for the degradation of organic dyes. RSC Adv. 2015;5:44128–44136. doi: 10.1039/C5RA06223C. - DOI
-
- Zhao Q., Long M., Li H., Wang L., Bai X., Zhang Y., Li D. Synthesis of Bi2MoO6 and Activating Peroxymonosulfate to Enhance Photocatalytic Activity under Visible Light Irradiation. Cryst. Res. Technol. 2021;56:2000219. doi: 10.1002/crat.202000219. - DOI
-
- Bai R., Yan W., Xiao Y., Wang S., Tian X., Li J., Xiao X., Lu X., Zhao F. Acceleration of peroxymonosulfate decomposition by a magnetic MoS2/CuFe2O4 heterogeneous catalyst for rapid degradation of fluoxetine. Chem. Eng. J. 2020;397:125501. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.125501. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

