Anti-Melanogenic Effects of Lilium lancifolium Root Extract via Downregulation of PKA/CREB and MAPK/CREB Signaling Pathways in B16F10 Cells
- PMID: 37960022
- PMCID: PMC10648933
- DOI: 10.3390/plants12213666
Anti-Melanogenic Effects of Lilium lancifolium Root Extract via Downregulation of PKA/CREB and MAPK/CREB Signaling Pathways in B16F10 Cells
Abstract
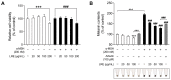
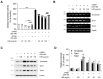
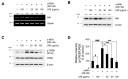
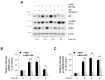
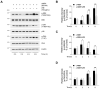
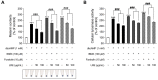
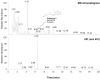
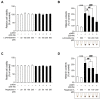
Hyperpigmentation disorders causing emotional distress require the topical use of depigmenting agents of natural origin. In this study, the anti-melanogenic effects of the Lilium lancifolium root extract (LRE) were investigated in B16F10 cells. Consequently, a non-cytotoxic concentration of the extract reduced intracellular melanin content and tyrosinase activity in a dose-dependent manner, correlating with the diminished expression of core melanogenic enzymes within cells. LRE treatment also inhibited cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) response element-binding protein (CREB)/microphthalmia-associated transcription factor signaling, which regulates the expression of tyrosinase-related genes. Upon examining these findings from a molecular mechanism perspective, LRE treatment suppressed the phosphorylation of protein kinase A (PKA), p38, and extracellular signal-related kinase (ERK), which are upstream regulators of CREB. In addition, L-phenylalanine and regaloside A, specifically identified within the LRE using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry, exhibited inhibitory effects on melanin production. Collectively, these results imply that LRE potentially suppresses cAMP-mediated melanogenesis by downregulating PKA/CREB and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/CREB signaling pathways. Therefore, it can be employed as a novel therapeutic ingredient of natural origin to ameliorate hyperpigmentation disorders.
Keywords: B16F10; L-phenylalanine; Lilium lancifolium; anti-melanogenic effect; melanin; melanogenesis; regaloside A; α-melanocyte stimulating hormone (α-MSH).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Swalwell H., Latimer J., Haywood R.M., Birch-Machin M.A. Investigating the role of melanin in UVA/UVB-and hydrogen peroxide-induced cellular and mitochondrial ROS production and mitochondrial DNA damage in human melanoma cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012;52:626–634. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2011.11.019. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

