Algal Bio-Stimulants Enhance Salt Tolerance in Common Bean: Dissecting Morphological, Physiological, and Genetic Mechanisms for Stress Adaptation
- PMID: 37960071
- PMCID: PMC10648064
- DOI: 10.3390/plants12213714
Algal Bio-Stimulants Enhance Salt Tolerance in Common Bean: Dissecting Morphological, Physiological, and Genetic Mechanisms for Stress Adaptation
Abstract
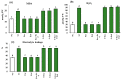
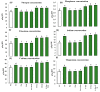
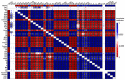
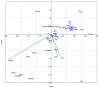
Salinity adversely affects the plant's morphological characteristics, but the utilization of aqueous algal extracts (AE) ameliorates this negative impact. In this study, the application of AE derived from Chlorella vulgaris and Dunaliella salina strains effectively reversed the decline in biomass allocation and water relations, both in normal and salt-stressed conditions. The simultaneous application of both extracts in salt-affected soil notably enhanced key parameters, such as chlorophyll content (15%), carotene content (1%), photosynthesis (25%), stomatal conductance (7%), and transpiration rate (23%), surpassing those observed in the application of both AE in salt-affected as compared to salinity stress control. Moreover, the AE treatments effectively mitigated lipid peroxidation and electrolyte leakage induced by salinity stress. The application of AE led to an increase in GB (6%) and the total concentration of free amino acids (47%) by comparing with salt-affected control. Additionally, salinity stress resulted in an elevation of antioxidant enzyme activities, including superoxide dismutase, ascorbate peroxidase, catalase, and glutathione reductase. Notably, the AE treatments significantly boosted the activity of these antioxidant enzymes under salinity conditions. Furthermore, salinity reduced mineral contents, but the application of AE effectively counteracted this decline, leading to increased mineral levels. In conclusion, the application of aqueous algal extracts, specifically those obtained from Chlorella vulgaris and Dunaliella salina strains, demonstrated significant efficacy in alleviating salinity-induced stress in Phaseolus vulgaris plants.
Keywords: Chlorella vulgaris; Dunaliella salina; Phaseolus vulgaris; antioxidants; osmolytes; photosynthesis; salinity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Loudière D., Gourbesville P. World Water Development Report-Water and Climate Change. Houille Blanche. 2020;2020:76–81. doi: 10.1051/lhb/2020024. - DOI
-
- Ahanger M.A., Ahmad P. Plant Signaling Molecules. Elsevier; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2019. Role of Mineral Nutrients in Abiotic Stress Tolerance; pp. 269–285.
-
- Ali M.M., Jeddi K., Attia M.S., Elsayed S.M., Yusuf M., Osman M.S., Soliman M.H., Hessini K. Wuxal amino (Bio stimulant) improved growth and physiological performance of tomato plants under salinity stress through adaptive mechanisms and antioxidant potential. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2021;28:3204–3213. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.04.040. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kaya C., Higgs D., Ashraf M., Alyemeni M.N., Ahmad P. Integrative roles of nitric oxide and hydrogen sulfide in melatonin-induced tolerance of pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) plants to iron deficiency and salt stress alone or in combination. Physiol. Plant. 2020;168:256–277. doi: 10.1111/ppl.12976. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

