Efficacy and Safety of a High-Energy, Low-Protein Formula Replacement Meal for Pre-Dialysis Chronic Kidney Disease Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 37960159
- PMCID: PMC10648072
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15214506
Efficacy and Safety of a High-Energy, Low-Protein Formula Replacement Meal for Pre-Dialysis Chronic Kidney Disease Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
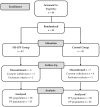
High-energy, low-protein formulas (HE-LPFs) are commonly used as oral nutritional supplements (ONSs) to help provide extra calories to patients who are adhering to a low-protein diet (LPD) after diagnosis with chronic kidney disease (CKD). This randomized controlled trial aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of an HE-LPF as either a partial or a total replacement for one meal in pre-dialysis CKD patients. Stage 4-5 CKD patients received either a once-daily HE-LPF (HE-LPF group) or normal food (control group) for a period of 4 weeks while following an LPD. Overall, 73 patients who completed the study were included in the intention-to-treat population. After analyzing the 3-day food records, the HE-LPF group experienced a significant decrease in the percentage of energy derived from protein (p < 0.05) and an increase in the percentage of energy derived from fat (p < 0.05) compared to the control group. The two groups had no significant differences in body weight, body composition, grip strength, renal function, electrolytes, or metabolic markers. The HE-LPF group had a high adherence (94.9% at week 4), and no adverse effects were observed. HE-LPFs are safe to employ as meal replacements for pre-dialysis CKD patients adhering to an LPD.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; low-protein diet; meal replacement; oral nutritional supplement.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ikizler T.A., Burrowes J.D., Byham-Gray L.D., Campbell K.L., Carrero J.J., Chan W., Fouque D., Friedman A.N., Ghaddar S., Goldstein-Fuchs D.J., et al. KDOQI Clinical Practice Guideline for Nutrition in CKD: 2020 Update. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020;76:S1–S107. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2020.05.006. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

