Fish Oil Supplementation with Resistance Exercise Training Enhances Physical Function and Cardiometabolic Health in Postmenopausal Women
- PMID: 37960168
- PMCID: PMC10650161
- DOI: 10.3390/nu15214516
Fish Oil Supplementation with Resistance Exercise Training Enhances Physical Function and Cardiometabolic Health in Postmenopausal Women
Abstract
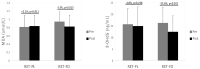
Menopause is a condition associated with an increased risk of dysregulation in cardiovascular and metabolic health among older women. While fish oil (FO) has garnered great attention for its health-enhancing properties, its potential for enhancing cardiometabolic health in this demographic remains to be established. The purpose of this study was to determine the clinical efficacy of an 8 wk administration of FO combined with programmed resistance exercise training (RET) on physical function and risk factors associated with cardiometabolic health in healthy older women. Twenty, healthy, older women were randomly assigned to one of the two experimental groups: resistance training with placebo (RET-PL) or RET with fish oil (RET-FO). Physical function, blood pressure (BP), triglyceride (TG), and systemic inflammation and oxidative stress biomarkers were assessed before and after the intervention. Statistical significance was set at p ≤ 0.05. Physical function was greatly enhanced in both RET and RET-FO. Handgrip strength substantially increased only in RET-FO. RET-FO exhibited significant decreases in BP, TG, inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α and IL-6), and oxidative stress (MDA and 8-OHdG) levels, while no detectable changes were found in RET-PL. Our findings indicate that FO administration during 8 wks of RET appears to enhance muscle function and lower risk factors linked to cardiometabolic disorders in postmenopausal women.
Keywords: blood pressure; fish oil; inflammation; oxidative stress; physical function; resistance exercise training.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

