A Portable Three-Layer Compton Camera for Wide-Energy-Range Gamma-ray Imaging: Design, Simulation and Preliminary Testing
- PMID: 37960650
- PMCID: PMC10647430
- DOI: 10.3390/s23218951
A Portable Three-Layer Compton Camera for Wide-Energy-Range Gamma-ray Imaging: Design, Simulation and Preliminary Testing
Abstract
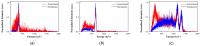
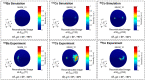
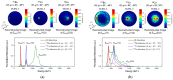
(1) Background: The imaging energy range of a typical Compton camera is limited due to the fact that scattered gamma photons are seldom fully absorbed when the incident energies are above 3 MeV. Further improving the upper energy limit of gamma-ray imaging has important application significance in the active interrogation of special nuclear materials and chemical warfare agents, as well as range verification of proton therapy. (2) Methods: To realize gamma-ray imaging in a wide energy range of 0.3~7 MeV, a principle prototype, named a portable three-layer Compton camera, is developed using the scintillation detector that consists of an silicon photomultiplier array coupled with a Gd3Al2Ga3O12:Ce pixelated scintillator array. Implemented in a list-mode maximum likelihood expectation maximization algorithm, a far-field energy-domain imaging method based on the two interaction events is applied to estimate the initial energy and spatial distribution of gamma-ray sources. The simulation model of the detectors is established based on the Monte Carlo simulation toolkit Geant4. The reconstructed images of a 133Ba, a 137Cs and a 60Co point-like sources have been successfully obtained with our prototype in laboratory tests and compared with simulation studies. (3) Results: The proportion of effective imaging events accounts for about 2%, which allows our prototype to realize the reconstruction of the distribution of a 0.05 μSv/h 137Cs source in 10 s. The angular resolution for resolving two 137Cs point-like sources is 15°. Additional simulated imaging of the 6.13 MeV gamma-rays from 14.1 MeV neutron scattering with water preliminarily demonstrates the imaging capability for high incident energy. (4) Conclusions: We conclude that the prototype has a good imaging performance in a wide energy range (0.3~7 MeV), which shows potential in several MeV gamma-ray imaging applications.
Keywords: Compton camera; Monte Carlo simulation; image reconstruction; scintillation detector; wide energy range.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures












Similar articles
-
A hybrid coded-aperture and Compton camera based on cerium-doped Gd3Al2Ga3O12 scintillators coupled with multi-pixel photon counter arrays.Rev Sci Instrum. 2022 Nov 1;93(11):113103. doi: 10.1063/5.0097257. Rev Sci Instrum. 2022. PMID: 36461454
-
Image reconstruction for a multi-layer Compton telescope: an analytical model for three interaction events.Phys Med Biol. 2020 Jul 13;65(14):145005. doi: 10.1088/1361-6560/ab8cd4. Phys Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32330911
-
Performance demonstration of a hybrid Compton camera with an active pinhole for wide-band X-ray and gamma-ray imaging.Sci Rep. 2020 Aug 20;10(1):14064. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-71019-5. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32820211 Free PMC article.
-
Development and Applications of Compton Camera-A Review.Sensors (Basel). 2022 Sep 28;22(19):7374. doi: 10.3390/s22197374. Sensors (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36236474 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Compton imaging for medical applications.Radiol Phys Technol. 2022 Sep;15(3):187-205. doi: 10.1007/s12194-022-00666-2. Epub 2022 Jul 22. Radiol Phys Technol. 2022. PMID: 35867197 Review.
References
-
- De Angelis A., Tatischeff V., Argan A., Brandt S., Bulgarelli A., Bykov A., Costantini E., Curadoda Silva R., Grenier I.A., Hanlon L., et al. Gamma-ray astrophysics in the MeV range: The ASTROGAM concept and beyond. Exp. Astron. 2021;51:1225–1254. doi: 10.1007/s10686-021-09706-y. - DOI
-
- Mochizuki S., Kataoka J., Koide A., Fujieda K., Maruhashi T., Kurihara T., Sueoka K., Tagawa L., Yoneyama M., Inaniwa T. High-precision Compton imaging of 4.4 MeV prompt gamma-ray toward an on-line monitor for proton therapy. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. A. 2019;936:43–45. doi: 10.1016/j.nima.2018.11.032. - DOI
-
- Fontana M., Ley J.L., Dauvergne D., Freud N., Krimmer J., Létang J.M., Maxim V., Richard M.-H., Rinaldi I., Testa É. Monitoring ion beam therapy with a Compton camera: Simulation studies of the clinical feasibility. IEEE Trans. Radiat. Plasma Med. Sci. 2020;4:218–232. doi: 10.1109/TRPMS.2019.2933985. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

