This is a preprint.
Phenotypic complexities of rare heterozygous neurexin-1 deletions
- PMID: 37961635
- PMCID: PMC10634884
- DOI: 10.1101/2023.10.28.564543
Phenotypic complexities of rare heterozygous neurexin-1 deletions
Update in
-
Phenotypic complexities of rare heterozygous neurexin-1 deletions.Nature. 2025 Jun;642(8068):710-720. doi: 10.1038/s41586-025-08864-9. Epub 2025 Apr 9. Nature. 2025. PMID: 40205044
Abstract
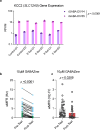
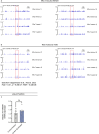
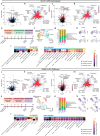
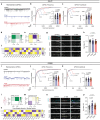
Given the large number of genes significantly associated with risk for neuropsychiatric disorders, a critical unanswered question is the extent to which diverse mutations --sometimes impacting the same gene-- will require tailored therapeutic strategies. Here we consider this in the context of rare neuropsychiatric disorder-associated copy number variants (2p16.3) resulting in heterozygous deletions in NRXN1, a pre-synaptic cell adhesion protein that serves as a critical synaptic organizer in the brain. Complex patterns of NRXN1 alternative splicing are fundamental to establishing diverse neurocircuitry, vary between the cell types of the brain, and are differentially impacted by unique (non-recurrent) deletions. We contrast the cell-type-specific impact of patient-specific mutations in NRXN1 using human induced pluripotent stem cells, finding that perturbations in NRXN1 splicing result in divergent cell-type-specific synaptic outcomes. Via distinct loss-of-function (LOF) and gain-of-function (GOF) mechanisms, NRXN1 +/- deletions cause decreased synaptic activity in glutamatergic neurons, yet increased synaptic activity in GABAergic neurons. Reciprocal isogenic manipulations causally demonstrate that aberrant splicing drives these changes in synaptic activity. For NRXN1 deletions, and perhaps more broadly, precision medicine will require stratifying patients based on whether their gene mutations act through LOF or GOF mechanisms, in order to achieve individualized restoration of NRXN1 isoform repertoires by increasing wildtype, or ablating mutant isoforms. Given the increasing number of mutations predicted to engender both LOF and GOF mechanisms in brain disorders, our findings add nuance to future considerations of precision medicine.
Keywords: GABAergic neurons; Human induced pluripotent stem cells; NRXN1; alternative splicing; disease modeling; genomics; glutamatergic neurons; neuropsychiatric disorder; precision medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics declarations / Competing interest statement. All authors have no competing interests to declare.
Figures










References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
