Effects of the HIV-1 maturation inhibitor GSK3640254 on QT interval in healthy participants
- PMID: 37961928
- PMCID: PMC10644204
- DOI: 10.1002/prp2.1151
Effects of the HIV-1 maturation inhibitor GSK3640254 on QT interval in healthy participants
Abstract
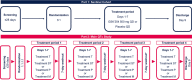
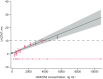
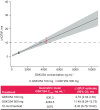
GSK3640254 (GSK'254) is a novel HIV-1 maturation inhibitor with pharmacokinetics supporting once-daily (QD) therapy for HIV-1 treatment. This thorough QT/corrected QT (QTc) study evaluated the effect of GSK'254 on cardiac repolarization. In this two-part, randomized study, healthy participants received GSK'254 or placebo QD for 7 days (part 1) to determine safety and pharmacokinetics of a 500-mg supratherapeutic dose. Four sequential treatment periods composed the main QTc study (part 2): GSK'254 100 mg, GSK'254 500 mg, placebo QD for 7 days, or placebo QD for 6 days with a 400-mg moxifloxacin dose on Day 7 (all with a moderate-fat meal). Concentration-QTc analyses modeled the relationship between GSK'254 plasma concentrations and placebo-adjusted change from baseline in QT interval corrected with Fridericia's formula (ΔΔQTcF). Of 50 participants enrolled, 48 completed the study (part 1, 8/8; part 2, 40/42). Least-squares (LS) mean change from baseline in QTcF for GSK'254 100 mg followed the placebo pattern across time points (maximum LS mean ΔΔQTcF, 1.7 ms); the upper bound of the 90% CI remained <10 ms. Maximum LS mean ΔΔQTcF for GSK'254 500 mg exceeded the 10-ms threshold: 10.6 ms (90% CI 7.75-13.38). Neither GSK'254 dose had clinically relevant effects on heart rate or cardiac conduction. By concentration-QTc analysis, no effect on ΔΔQTcF >10 ms is expected up to GSK'254 concentrations of ~3070 ng mL-1 . No clinically relevant effects on cardiac parameters were seen in healthy participants with GSK'254 at the 100-mg dose.
Keywords: QT prolongation; antiretrovirals; drug safety; phase I.
© 2023 ViiV Healthcare. Pharmacology Research & Perspectives published by British Pharmacological Society and American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
YZ, MB, PY, JZ, BW, VB, BRW, SJ, and ML are or were employees of GSK or ViiV Healthcare at the time of the study and may hold stock in GSK.
Figures
References
-
- Joshi SR, Fernando D, Igwe S, et al. The initial phase I evaluation of the safety, tolerability, and pharmacokinetics of GSK3640254, a next‐generation HIV maturation inhibitor, as assessed in healthy subjects. Abstract presented at: EACS 2019; May 14–16, 2019; Noordwijk, the Netherlands.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

