Adenovirus E1A binding to DCAF10 targets proteasomal degradation of RUVBL1/2 AAA+ ATPases required for quaternary assembly of multiprotein machines, innate immunity, and responses to metabolic stress
- PMID: 37962355
- PMCID: PMC10734532
- DOI: 10.1128/jvi.00993-23
Adenovirus E1A binding to DCAF10 targets proteasomal degradation of RUVBL1/2 AAA+ ATPases required for quaternary assembly of multiprotein machines, innate immunity, and responses to metabolic stress
Abstract
Inactivation of EP300/CREBB paralogous cellular lysine acetyltransferases (KATs) during the early phase of infection is a consistent feature of DNA viruses. The cell responds by stabilizing transcription factor IRF3 which activates transcription of scores of interferon-stimulated genes (ISGs), inhibiting viral replication. Human respiratory adenoviruses counter this by assembling a CUL4-based ubiquitin ligase complex that polyubiquitinylates RUVBL1 and 2 inducing their proteasomal degradation. This inhibits accumulation of active IRF3 and the expression of anti-viral ISGs, allowing replication of the respiratory HAdVs in the face of inhibition of EP300/CBEBBP KAT activity by the N-terminal region of E1A.
Keywords: CBP; CRL4; DCAF10; E1A; IRF3; P300; adenovirus; innate immunity; virology.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
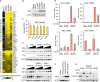
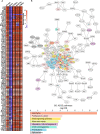
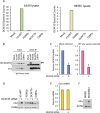
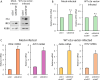
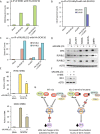
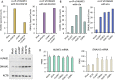
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

