PathBank 2.0-the pathway database for model organism metabolomics
- PMID: 37962386
- PMCID: PMC10767802
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkad1041
PathBank 2.0-the pathway database for model organism metabolomics
Erratum in
-
Correction to 'PathBank 2.0-the pathway database for model organism metabolomics'.Nucleic Acids Res. 2024 Apr 12;52(6):3486. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkae191. Nucleic Acids Res. 2024. PMID: 38471813 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
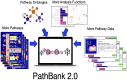
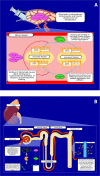
PathBank (https://pathbank.org) and its predecessor database, the Small Molecule Pathway Database (SMPDB), have been providing comprehensive metabolite pathway information for the metabolomics community since 2010. Over the past 14 years, these pathway databases have grown and evolved significantly to meet the needs of the metabolomics community and respond to continuing changes in computing technology. This year's update, PathBank 2.0, brings a number of important improvements and upgrades that should make the database more useful and more appealing to a larger cross-section of users. In particular, these improvements include: (i) a significant increase in the number of primary or canonical pathways (from 1720 to 6951); (ii) a massive increase in the total number of pathways (from 110 234 to 605 359); (iii) significant improvements to the quality of pathway diagrams and pathway descriptions; (iv) a strong emphasis on drug metabolism and drug mechanism pathways; (v) making most pathway images more slide-compatible and manuscript-compatible; (vi) adding tools to support better pathway filtering and selecting through a more complete pathway taxonomy; (vii) adding pathway analysis tools for visualizing and calculating pathway enrichment. Many other minor improvements and updates to the content, the interface and general performance of the PathBank website have also been made. Overall, we believe these upgrades and updates should greatly enhance PathBank's ease of use and its potential applications for interpreting metabolomics data.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures


References
-
- Heckendorf C., Blum B.C., Lin W., Lawton M.L., Emili A. Integration of metabolomic and proteomic data to uncover actionable metabolic pathways. Methods Mol. Biol. 2023; 2660:137–148. - PubMed
-
- Cavill R., Jennen D., Kleinjans J., Briedé J.J. Transcriptomic and metabolomic data integration. Brief. Bioinform. 2016; 17:891–901. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

