A developmental account of the role of sequential dependencies in typical and atypical language learners
- PMID: 37963089
- PMCID: PMC10939949
- DOI: 10.1080/02643294.2023.2275837
A developmental account of the role of sequential dependencies in typical and atypical language learners
Abstract
The Gerken lab has shown that infants are able to learn sound patterns that obligate local sequential dependencies that are no longer readily accessible to adults. The Goffman lab has shown that children with developmental language disorder (DLD) exhibit deficits in learning sequential dependencies that influence the acquisition of words and grammar, as well as other types of domain general sequences. Thus, DLD appears to be an impaired ability to detect and deploy sequential dependencies over multiple domains. We meld these two lines of research to propose a novel account in which sequential dependency learning is required for many phonological and morphosyntactic patterns in natural language and is also central to the language and domain general deficits that are attested in DLD. However, patterns that are not dependent on sequential dependencies but rather on networks of stored forms are learnable by children with DLD as well as by adults.
Keywords: Language development; artificial grammar; developmental language disorder; infants; motor skill; phonotactics; sequencing.
Figures
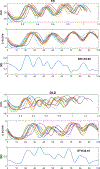
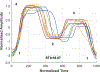
References
-
- Anderson ND, & Dell GS (2018). The role of consolidation in learning context-dependent phonotactic patterns in speech and digital sequence production. PNAS Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 115(14), 3617–3622. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1721107115 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bedore LM, & Leonard LB (2001). Grammatical morphology deficits in Spanish-speaking children with specific language impairment. Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research, 44,905–924. PMID: 11521782 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
