Deep mutational scanning of proteins in mammalian cells
- PMID: 37963462
- PMCID: PMC10694495
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2023.100641
Deep mutational scanning of proteins in mammalian cells
Abstract
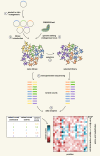
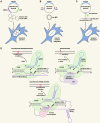
Protein mutagenesis is essential for unveiling the molecular mechanisms underlying protein function in health, disease, and evolution. In the past decade, deep mutational scanning methods have evolved to support the functional analysis of nearly all possible single-amino acid changes in a protein of interest. While historically these methods were developed in lower organisms such as E. coli and yeast, recent technological advancements have resulted in the increased use of mammalian cells, particularly for studying proteins involved in human disease. These advancements will aid significantly in the classification and interpretation of variants of unknown significance, which are being discovered at large scale due to the current surge in the use of whole-genome sequencing in clinical contexts. Here, we explore the experimental aspects of deep mutational scanning studies in mammalian cells and report the different methods used in each step of the workflow, ultimately providing a useful guide toward the design of such studies.
Keywords: CP: Biotechnology; CP: Genetics; deep mutational scanning; genome editing; mammalian; saturation mutagenesis; structure/function analysis; variants of unknown significance.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Deep Mutational Scanning in Disease-related Genes with Saturation Mutagenesis-Reinforced Functional Assays (SMuRF).bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 25:2023.07.12.548370. doi: 10.1101/2023.07.12.548370. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Cell. 2024 Nov 14;187(23):6707-6724.e22. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.08.047. PMID: 37873263 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Exploring the functional residues in a flavin-binding fluorescent protein using deep mutational scanning.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 2;9(6):e97817. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097817. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24887409 Free PMC article.
-
Deep mutational scanning: A versatile tool in systematically mapping genotypes to phenotypes.Front Genet. 2023 Jan 12;14:1087267. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1087267. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 36713072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rational Protein Engineering Guided by Deep Mutational Scanning.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Sep 23;16(9):23094-110. doi: 10.3390/ijms160923094. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26404267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Saturation mutagenesis-reinforced functional assays for disease-related genes.Cell. 2024 Nov 14;187(23):6707-6724.e22. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.08.047. Epub 2024 Sep 25. Cell. 2024. PMID: 39326416
Cited by
-
Image-based, pooled phenotyping reveals multidimensional, disease-specific variant effects.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jul 5:2025.07.03.663081. doi: 10.1101/2025.07.03.663081. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40631108 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
A side-by-side comparison of variant function measurements using deep mutational scanning and base editing.Nucleic Acids Res. 2025 Jul 19;53(14):gkaf738. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaf738. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025. PMID: 40744495 Free PMC article.
-
Computationally guided high-throughput engineering of an anti-CRISPR protein for precise genome editing in human cells.Cell Rep Methods. 2024 Oct 21;4(10):100882. doi: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2024.100882. Cell Rep Methods. 2024. PMID: 39437714 Free PMC article.
-
Mutational scanning of CRX classifies clinical variants and reveals biochemical properties of the transcriptional effector domain.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Mar 27:2024.03.21.585809. doi: 10.1101/2024.03.21.585809. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Genome Res. 2024 Oct 29;34(10):1540-1552. doi: 10.1101/gr.279415.124. PMID: 38585983 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Deep CRISPR mutagenesis characterizes the functional diversity of TP53 mutations.Nat Genet. 2025 Jan;57(1):140-153. doi: 10.1038/s41588-024-02039-4. Epub 2025 Jan 7. Nat Genet. 2025. PMID: 39774325 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Groot-Kormelink P.J., Ferrand S., Kelley N., Bill A., Freuler F., Imbert P.-E., Marelli A., Gerwin N., Sivilotti L.G., Miraglia L., et al. High Throughput Random Mutagenesis and Single Molecule Real Time Sequencing of the Muscle Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor. PLoS One. 2016;11 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0163129. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

