Instant processing of large-scale image data with FACT, a real-time cell segmentation and tracking algorithm
- PMID: 37963463
- PMCID: PMC10694492
- DOI: 10.1016/j.crmeth.2023.100636
Instant processing of large-scale image data with FACT, a real-time cell segmentation and tracking algorithm
Abstract
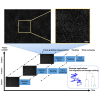
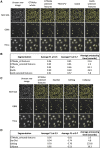
Quantifying cellular characteristics from a large heterogeneous population is essential to identify rare, disease-driving cells. A recent development in the combination of high-throughput screening microscopy with single-cell profiling provides an unprecedented opportunity to decipher disease-driving phenotypes. Accurately and instantly processing large amounts of image data, however, remains a technical challenge when an analysis output is required minutes after data acquisition. Here, we present fast and accurate real-time cell tracking (FACT). FACT can segment ∼20,000 cells in an average of 2.5 s (1.9-93.5 times faster than the state of the art). It can export quantifiable features minutes after data acquisition (independent of the number of acquired image frames) with an average of 90%-96% precision. We apply FACT to identify directionally migrating glioblastoma cells with 96% precision and irregular cell lineages from a 24 h movie with an average F1 score of 0.91.
Keywords: CP: Imaging; cell tracking correction; high-throughput imaging; lineage tracking; live-cell imaging; machine-learning-based cell segmentation; real-time cell tracking.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






References
-
- You L., Su P.-R., Betjes M., Rad R.G., Chou T.-C., Beerens C., van Oosten E., Leufkens F., Gasecka P., Muraro M., et al. Linking the genotypes and phenotypes of cancer cells in heterogenous populations via real-time optical tagging and image analysis. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2022;6:667–675. doi: 10.1038/s41551-022-00853-x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

