Functional recovery in a cohort of ECMO and non-ECMO acute respiratory distress syndrome survivors
- PMID: 37964311
- PMCID: PMC10644522
- DOI: 10.1186/s13054-023-04724-y
Functional recovery in a cohort of ECMO and non-ECMO acute respiratory distress syndrome survivors
Abstract
Background: The mortality benefit of VV-ECMO in ARDS has been extensively studied, but the impact on long-term functional outcomes of survivors is poorly defined. We aimed to assess the association between ECMO and functional outcomes in a contemporaneous cohort of survivors of ARDS.
Methods: Multicenter retrospective cohort study of ARDS survivors who presented to follow-up clinic. The primary outcome was FVC% predicted. Univariate and multivariate regression models were used to evaluate the impact of ECMO on the primary outcome.
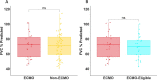
Results: This study enrolled 110 survivors of ARDS, 34 of whom were managed using ECMO. The ECMO cohort was younger (35 [28, 50] vs. 51 [44, 61] years old, p < 0.01), less likely to have COVID-19 (58% vs. 96%, p < 0.01), more severely ill based on the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score (7 [5, 9] vs. 4 [3, 6], p < 0.01), dynamic lung compliance (15 mL/cmH20 [11, 20] vs. 27 mL/cmH20 [23, 35], p < 0.01), oxygenation index (26 [22, 33] vs. 9 [6, 11], p < 0.01), and their need for rescue modes of ventilation. ECMO patients had significantly longer lengths of hospitalization (46 [27, 62] vs. 16 [12, 31] days, p < 0.01) ICU stay (29 [19, 43] vs. 10 [5, 17] days, p < 0.01), and duration of mechanical ventilation (24 [14, 42] vs. 10 [7, 17] days, p < 0.01). Functional outcomes were similar in ECMO and non-ECMO patients. ECMO did not predict changes in lung function when adjusting for age, SOFA, COVID-19 status, or length of hospitalization.
Conclusions: There were no significant differences in the FVC% predicted, or other markers of pulmonary, neurocognitive, or psychiatric functional recovery outcomes, when comparing a contemporaneous clinic-based cohort of survivors of ARDS managed with ECMO to those without ECMO.
Keywords: ARDS; COVID-19; ECMO; Functional recovery; Long-term outcomes; Pulmonary function tests.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
JHC has served on the speakers bureau for La Jolla, Pharmaceutical Company and has received consulting fees from Exthera Medical, outside the scope of the submitted work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessment of 1-year Outcomes in Survivors of Severe Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Receiving Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation or Mechanical Ventilation: A Prospective Observational Study.Chin Med J (Engl). 2017 May 20;130(10):1161-1168. doi: 10.4103/0366-6999.205847. Chin Med J (Engl). 2017. PMID: 28485315 Free PMC article.
-
Risk Factors of Mortality for Patients Receiving Venovenous Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation for COVID-19 Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome.Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2021 Dec;22(10):1086-1092. doi: 10.1089/sur.2021.114. Epub 2021 Sep 6. Surg Infect (Larchmt). 2021. PMID: 34494893
-
Analysis of COVID-19 Patients With Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome Managed With Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation at US Academic Centers.Ann Surg. 2021 Jul 1;274(1):40-44. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0000000000004870. Ann Surg. 2021. PMID: 33843791 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Term Quality of Life After Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in ARDS Survivors: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Intensive Care Med. 2020 Mar;35(3):233-243. doi: 10.1177/0885066617737035. Epub 2017 Oct 19. J Intensive Care Med. 2020. PMID: 29050526
-
Relationship between the Pre-ECMO and ECMO Time and Survival of Severe COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.J Clin Med. 2024 Feb 1;13(3):868. doi: 10.3390/jcm13030868. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38337562 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Outcomes of Severe ARDS COVID-19 Patients Denied for Venovenous ECMO Support: A Prospective Observational Comparative Study.J Clin Med. 2024 Mar 5;13(5):1493. doi: 10.3390/jcm13051493. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38592410 Free PMC article.
-
Long-term lung function recovery after ECMO versus non-ECMO management in acute respiratory failure: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Pulm Med. 2024 Oct 10;24(1):504. doi: 10.1186/s12890-024-03321-1. BMC Pulm Med. 2024. PMID: 39390464 Free PMC article.
References
-
- ECMO Registry of the Extracorporeal Life Support Organization (ELSO).
-
- Hajage D, Combes A, Guervilly C, Lebreton G, Mercat A, Pavot A, et al. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for severe acute respiratory distress syndrome associated with COVID-19: an emulated target trial analysis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2022;206(3):281–294. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202111-2495OC. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Peek GJ, Mugford M, Tiruvoipati R, Wilson A, Allen E, Thalanany MM, et al. Efficacy and economic assessment of conventional ventilatory support versus extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for severe adult respiratory failure (CESAR): a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2009;374(9698):1351–1363. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)61069-2. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Goligher EC, Tomlinson G, Hajage D, Wijeysundera DN, Fan E, Jüni P, et al. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for severe acute respiratory distress syndrome and posterior probability of mortality benefit in a post hoc bayesian analysis of a randomized clinical trial. JAMA. 2018;320(21):2251–2259. doi: 10.1001/jama.2018.14276. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical