The efficacy of sorafenib against hepatocellular carcinoma is enhanced by 5-aza-mediated inhibition of ID1 promoter methylation
- PMID: 37964494
- PMCID: PMC10761934
- DOI: 10.1002/2211-5463.13734
The efficacy of sorafenib against hepatocellular carcinoma is enhanced by 5-aza-mediated inhibition of ID1 promoter methylation
Abstract
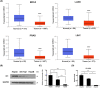
Sorafenib resistance greatly restricts its clinical application in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Numerous studies have reported that ID1 exerts a crucial effect in cancer initiation and development. Our previous research revealed an inhibitory role of ID1 in sorafenib resistance. However, the upstream regulatory mechanism of ID1 expression is unclear. Here, we discovered that ID1 expression is negatively correlated with promoter methylation, which is regulated by DNMT3B. Knockdown of DNMT3B significantly inhibited ID1 methylation status and resulted in an increase of ID1 expression. The demethylating agent 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine (5-aza) remarkably upregulated ID1 expression. The combination of 5-aza with sorafenib showed a synergistic effect on the inhibition of cell viability.
Keywords: DNA methylation; ID1; drug resistance; hepatocellular carcinoma; sorafenib.
© 2023 The Authors. FEBS Open Bio published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A et al. (2008) Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med 359, 378–390. - PubMed
-
- Beyeler S, Joly S, Fries M, Obermair FJ, Burn F, Mehmood R, Tabatabai G and Raineteau O (2014) Targeting the bHLH transcriptional networks by mutated E proteins in experimental glioma. Stem Cells 32, 2583–2595. - PubMed
-
- Tsigelny IF, Kouznetsova VL, Pingle SC and Kesari S (2014) bHLH transcription factors inhibitors for cancer therapy: general features for in silico drug design. Curr Med Chem 21, 3227–3243. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

