Blockade of IL-18Rα-mediated signaling pathway exacerbates neutrophil infiltration in imiquimod-induced psoriasis murine model
- PMID: 37964882
- PMCID: PMC10641785
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1293132
Blockade of IL-18Rα-mediated signaling pathway exacerbates neutrophil infiltration in imiquimod-induced psoriasis murine model
Abstract
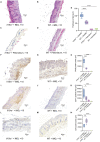
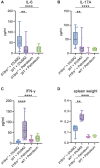
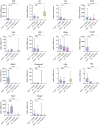
Psoriasis is an immune-mediated inflammatory disease of the skin, which is characterized by epidermal hyperkeratosis and neutrophil infiltration. The interleukin (IL)-17/IL-23 pathway and associated cytokines play major roles in the pathogenesis and exacerbation of psoriasis. The IL-18/IL-18 receptor (R) α signaling pathway is important for Th1 cytokine production and differentiation of Th1 cells; however, its role in the pathogenesis of psoriasis remains unknown. In this study, we investigated the effect of the IL-18Rα-mediated signaling pathway in the pathogenesis of psoriasis in Il18ra-deficient mice (Il18ra-/-) and wild-type imiquimod (IMQ)-induced psoriatic dermatitis model mice. Blocking this pathway exacerbated IMQ-induced psoriatic skin inflammation. Il18ra deficiency led to significant increases in the levels of IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, IL-17A, IL-23, and chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 2 in skin lesions. Gr1-positive cells highly infiltrated psoriatic skin lesions in Il18ra-/- mice compared to those in wild-type mice. Citrullinated histone H3-positive area was relatively broad in Il18ra-/- mice. These results suggest that IL-18Rα-mediated signaling pathways may inhibit psoriatic skin inflammation by regulating infiltration and activation of neutrophil and other innate immune cells.
Keywords: IL-18Rα; immune-mediated inflammatory disease; innate immunity; neutrophil; psoriasis.
Copyright © 2023 Akazawa, Nozaki, Yamazawa, Ishimura, Ashida, Okada, Kinoshita and Matsumura.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

