Single-cell transcriptomics reveals subtype-specific molecular profiles in Nrf2-deficient macrophages from murine atherosclerotic aortas
- PMID: 37965327
- PMCID: PMC10641521
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1249379
Single-cell transcriptomics reveals subtype-specific molecular profiles in Nrf2-deficient macrophages from murine atherosclerotic aortas
Abstract
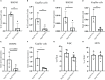
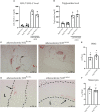
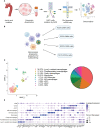
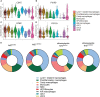
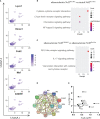
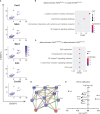
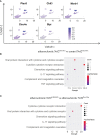
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) is a transcriptional regulator of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory response in all cell types. It also activates the transcription of genes important for macrophage function. Nrf2 activity declines with age and has been closely linked to atherosclerosis, but its specific role in this vascular pathology is not clear. Atherosclerotic plaques contain several macrophage subsets with distinct, yet not completely understood, functions in the lesion development. The aim of this study was to analyze the transcriptome of diverse Nrf2-deficient macrophage subpopulations from murine atherosclerotic aortas. Mice with transcriptionally inactive Nrf2 in Cdh5-expressing cells (Nrf2 Cdh5tKO) were used in the experiments. These mice lack transcriptional Nrf2 activity in endothelial cells, but also in a proportion of leukocytes. We confirmed that the bone marrow-derived and tissue-resident macrophages isolated from Nrf2 Cdh5tKO mice exhibit a significant decline in Nrf2 activity. Atherosclerosis was induced in Nrf2 Cdh5tKO and appropriate control mice via adeno-associated viral vector (AAV)-mediated overexpression of murine proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 (Pcsk9) in the liver and high-fat diet feeding. After 21 weeks, live aortic cells were sorted on FACS and single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) was performed. Unsupervised clustering singled out 13 distinct aortic cell types. Among macrophages, 9 subclusters were identified. Differential gene expression analysis revealed cell subtype-specific expression patterns. A subset of inflammatory macrophages from atherosclerotic Nrf2 Cdh5tKO mice demonstrated downregulation of DNA replication genes (e.g. Mcm7, Lig1, Pola1) concomitant with upregulation of DNA damage sensor Atr gene. Atherosclerotic Nrf2 Cdh5tKO Lyve1+ resident macrophages showed strong upregulation of IFN-stimulated genes, as well as changes in the expression of death pathways-associated genes (Slc40a1, Bcl2a1). Furthermore, we observed subtype-specific expression of core ferroptosis genes (e.g. Cp, Hells, Slc40a1) in inflammatory versus tissue resident macrophages. This observation suggested a link between ferroptosis and inflammatory microenvironment appearing at a very early stage of atherogenesis. Our findings indicate that Nrf2 deficiency in aortic macrophages leads to subtype-specific transcriptomic changes associated with inflammation, iron homeostasis, cell injury or death pathways. This may help understanding the role of aging-associated decline of Nrf2 activity and the function of specific macrophage subtypes in atherosclerotic lesion development.
Keywords: Nrf2; atherosclerosis; heterogeneity; macrophages; monocytes; scRNA-seq.
Copyright © 2023 Sarad, Stefańska, Kraszewska, Szade, Sluimer, Błyszczuk, Dulak and Jaźwa-Kusior.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

