Langerhans cell histiocytosis: current advances in molecular pathogenesis
- PMID: 37965340
- PMCID: PMC10642229
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1275085
Langerhans cell histiocytosis: current advances in molecular pathogenesis
Abstract
Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH) is a rare and clinically heterogeneous hematological disease characterized by the accumulation of mononuclear phagocytes in various tissues and organs. LCH is often characterized by activating mutations of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway with BRAFV600E being the most recurrent mutation. Although this discovery has greatly helped in understanding the disease and in developing better investigational tools, the process of malignant transformation and the cell of origin are still not fully understood. In this review, we focus on the newest updates regarding the molecular pathogenesis of LCH and novel suggested pathways with treatment potential.
Keywords: BRAFV600E; MAP2K1; dendritic cells; langerhans cell histiocytosis; monocytes; oncogene; senescence.
Copyright © 2023 Sconocchia, Foßelteder, Sconocchia and Reinisch.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
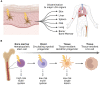
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

