Rat bite fever caused by Streptobacillus notomytis mimicking pyogenic polyarthritis: A case report
- PMID: 37965383
- PMCID: PMC10641602
- DOI: 10.1016/j.idcr.2023.e01923
Rat bite fever caused by Streptobacillus notomytis mimicking pyogenic polyarthritis: A case report
Abstract
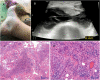
We report the world's sixth case of rat bite fever caused by Streptobacillus notomytis that mimicked pyogenic polyarthritis and required surgical debridement in combination with prolonged antibiotic therapy. This case report highlights the higher severity of rat bite fever caused by S. notomytis compared to S. moniliformis.
Keywords: Arthritis; Rat bite fever; Streptobacillus notomytis; Zoonosis.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

