Comparison of robotic-assisted versus conventional laparoscopic surgery in colorectal cancer resection: a systemic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- PMID: 37965455
- PMCID: PMC10641393
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1273378
Comparison of robotic-assisted versus conventional laparoscopic surgery in colorectal cancer resection: a systemic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Abstract
Introduction: There is still controversy on whether or not robot-assisted colorectal surgery (RACS) have advantages over laparoscopic-assisted colorectal surgery(LACS).
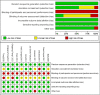
Materials and methods: The four databases (PubMed, Embase, Web of Science and Cochrane Library)were comprehensively searched for randomized controlled trials (RCTs) comparing the outcomes of RACS and LACS in the treatment of colorectal cancer from inception to 22 July 2023.
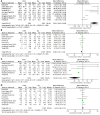
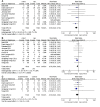
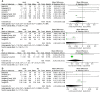
Results: Eleven RCTs were considered eligible for the meta-analysis. Compared with LACS,RACS has significantly longer operation time(MD=5.19,95%CI: 18.00,39.82, P<0.00001), but shorter hospital stay(MD=2.97,95%CI:-1.60,-0.33,P = 0.003),lower conversion rate(RR=3.62,95%CI:0.40,0.76,P = 0.0003), lower complication rate(RR=3.31,95%CI:0.64,0.89,P=0.0009),fewer blood loss(MD=2.71,95%CI:-33.24,-5.35,P = 0.007),lower reoperation rate(RR=2.12, 95%CI:0.33,0.96,P=0.03)and longer distal resection margin(MD=2.16, 95%CI:0.04,0.94, P = 0.03). There was no significantly difference in harvested lymph nodes, the time of first flatus, the time of first defecation,the time of first resume diet, proximal resection margin, readmission rates, mortalities and CRM+ rates between two group.
Conclusions: Our study indicated that RACS is a feasible and safe technique that can achieve better surgical efficacy compared with LACS in terms of short-term outcomes.
Systematic review registration: https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/prospero/, identifier CRD42023447088.
Keywords: colorectal cancer; complication; laparoscopic-assisted colorectal surgery; randomized controlled trial; robot-assisted colorectal surgery.
Copyright © 2023 Huang, Huang, Huang, Luo and Liang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- International Agency for Research on Cancer. World Health Organisation . Cancer today. In: Cancer fact sheets. (International Agency for Research on Cancer of World Health Organization). (2020). Available at: https://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/cancers/10_8_9-Colorectum-fact....
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

