Scaling law characteristics and spatiotemporal multicomponent analysis of syphilis from 2016 to 2022 in Zhejiang Province, China
- PMID: 37965512
- PMCID: PMC10642232
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2023.1275551
Scaling law characteristics and spatiotemporal multicomponent analysis of syphilis from 2016 to 2022 in Zhejiang Province, China
Abstract
Background: Syphilis has caused epidemics for hundreds of years, and the global syphilis situation remains serious. The reported incidence rate of syphilis in Zhejiang Province has ranked first in the province in terms of notifiable infectious diseases for many years and is the highest in China. This study attempts to use the scaling law theory to study the relationship between population size and different types of syphilis epidemics, while also exploring the main driving factors affecting the incidence of syphilis in different regions.
Methods: Data on syphilis cases and affected populations at the county level were obtained from the China Disease Control and Prevention Information System. The scaling relationship between different stages of syphilis and population size was explained by scaling law. The trend of the incidence from 2016 to 2022 was tested by the joinpoint regression. The index of distance between indices of simulation and observation (DISO) was applied to evaluate the overall performance of joinpoint regression model. Furthermore, a multivariate time series model was employed to identify the main driving components that affected the occurrence of syphilis at the county level. The p value less than 0.05 or confidence interval (CI) does not include 0 represented statistical significance for all the tests.
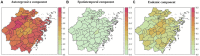
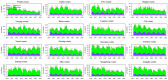
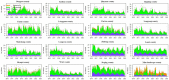
Results: From 2016 to 2022, a total of 204,719 cases of syphilis were reported in Zhejiang Province, including 2 deaths, all of which were congenital syphilis. Latent syphilis accounted for 79.47% of total syphilis cases. The annual percent change (APCs) of all types of syphilis, including primary syphilis, secondary syphilis, tertiary syphilis, congenital syphilis and latent syphilis, were - 21.70% (p < 0.001, 95% CI: -26.70 to -16.30), -16.80% (p < 0.001, 95% CI: -20.30 to -13.30), -8.70% (p < 0.001, 95% CI: -11.30 to -6.00), -39.00% (p = 0.001, 95% CI: -49.30 to -26.60) and - 7.10% (p = 0.008, 95% CI: -11.20 to -2.80), respectively. The combined scaling exponents of primary syphilis, secondary syphilis, tertiary syphilis, congenital syphilis and latent syphilis based on the random effects model were 0.95 (95% CI: 0.88 to 1.01), 1.14 (95% CI: 1.12 to 1.16), 0.43 (95% CI: 0.37 to 0.49), 0.0264 (95% CI: -0.0047 to 0.0575) and 0.88 (95% CI: 0.82 to 0.93), respectively. The overall average effect values of the endemic component, spatiotemporal component and autoregressive component for all counties were 0.24, 0.035 and 0.72, respectively. The values of the autoregressive component for most counties were greater than 0.7. The endemic component of the top 10 counties with the highest values was greater than 0.34. Two counties with value of the spatiotemporal component higher than 0.1 were Xihu landscape county and Shengsi county. From 2016 to 2022, the endemic and autoregressive components of each county showed obvious seasonal changes.
Conclusion: The scaling exponent had both temporal trend characteristics and significant heterogeneity in the association between each type of syphilis and population size. Primary syphilis and latent syphilis exhibited a linear pattern, secondary syphilis presented a superlinear pattern, and tertiary syphilis exhibited a sublinear pattern. This suggested that further prevention of infection and transmission among high-risk populations and improvement of diagnostic accuracy in underdeveloped areas is needed. The autoregressive components and the endemic components were the main driving factors that affected the occurrence of syphilis. Targeted prevention and control strategies must be developed based on the main driving modes of the epidemic in each county.
Keywords: epidemiology; joinpoint regression; multivariate time series model; scaling law; syphilis.
Copyright © 2023 Wu, Xue, Wu, Lu, Ding, Wang, Fu, Yang and Lin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Estimation of scrub typhus incidence and spatiotemporal multicomponent characteristics from 2016 to 2023 in Zhejiang Province, China.Front Public Health. 2024 Sep 26;12:1359318. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1359318. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39391156 Free PMC article.
-
Time series analysis and scaling law characteristics of viral hepatitis from 2004 to 2023 in Zhejiang Province, China.PLoS One. 2025 Mar 10;20(3):e0319642. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0319642. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40063651 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial-temporal characteristics of severe fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome and the relationship with meteorological factors from 2011 to 2018 in Zhejiang Province, China.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020 Apr 7;14(4):e0008186. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0008186. eCollection 2020 Apr. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2020. PMID: 32255791 Free PMC article.
-
Spatiotemporal characteristics and the epidemiology of tuberculosis in China from 2004 to 2017 by the nationwide surveillance system.BMC Public Health. 2020 Aug 26;20(1):1284. doi: 10.1186/s12889-020-09331-y. BMC Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32843011 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial-temporal characteristics and the epidemiology of haemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome from 2007 to 2016 in Zhejiang Province, China.Sci Rep. 2018 Jul 6;8(1):10244. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-28610-8. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29980717 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Clinical characteristics and cause analysis of false-positive results in treponemal testing among patients.Ann Med. 2025 Dec;57(1):2454327. doi: 10.1080/07853890.2025.2454327. Epub 2025 Jan 27. Ann Med. 2025. PMID: 39868671 Free PMC article.
-
Analysis of the trend of notifiable sexually transmitted infections in China between 2006-22.J Glob Health. 2025 Jun 27;15:04175. doi: 10.7189/jogh.15.04175. J Glob Health. 2025. PMID: 40570230 Free PMC article.
-
Estimation of scrub typhus incidence and spatiotemporal multicomponent characteristics from 2016 to 2023 in Zhejiang Province, China.Front Public Health. 2024 Sep 26;12:1359318. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2024.1359318. eCollection 2024. Front Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39391156 Free PMC article.
-
Age-period-cohort analysis of syphilis epidemics in Eastern China, China, 2005-2024.Front Public Health. 2025 Jul 7;13:1606491. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2025.1606491. eCollection 2025. Front Public Health. 2025. PMID: 40692887 Free PMC article.
-
Time series analysis and scaling law characteristics of viral hepatitis from 2004 to 2023 in Zhejiang Province, China.PLoS One. 2025 Mar 10;20(3):e0319642. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0319642. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40063651 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization . Global progress report on HIV, viral hepatitis and sexually transmitted infections, 2021 [EB/OL]. Available at: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789240027077 (Accessed February 16, 2023).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

