Effectiveness of the Original Monovalent Coronavirus Disease 2019 Vaccines in Preventing Emergency Department or Urgent Care Encounters and Hospitalizations Among Adults With Disabilities: VISION Network, June 2021-September 2022
- PMID: 37965644
- PMCID: PMC10642729
- DOI: 10.1093/ofid/ofad474
Effectiveness of the Original Monovalent Coronavirus Disease 2019 Vaccines in Preventing Emergency Department or Urgent Care Encounters and Hospitalizations Among Adults With Disabilities: VISION Network, June 2021-September 2022
Abstract
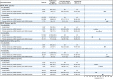
Adults with disabilities are at increased risk for severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Using data across 9 states during Delta- and Omicron-predominant periods (June 2021-September 2022), we evaluated the effectiveness of the original monovalent COVID-19 messenger RNA vaccines among 521 206 emergency department/urgent care encounters (11 471 [2%] in patients with a documented disability) and 139 548 hospitalizations (16 569 [12%] in patients with a disability) for laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 illness in adults (aged ≥18 years). Across variant periods and for the primary series or booster doses, vaccine effectiveness was similar in those with and those without a disability. These findings highlight the importance of adults with disabilities staying up to date with COVID-19 vaccinations.
Keywords: COVID-19; disabilities; test-negative design; vaccine effectiveness.
Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest. A. L. N. reports institutional support from Pfizer for an unrelated study of meningococcal B vaccine safety during pregnancy. N. P. K. reports institutional support from Pfizer, Merck, GlaxoSmithKline (GSK), Sanofi Pasteur, and Protein Sciences (now Sanofi Pasteur) for unrelated studies and institutional support from Pfizer for coronavirus disease 2019 vaccine clinical trials. All other authors report no potential conflicts.
Figures

References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Disability inclusion: disability and health promotion. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/disabilityandhealth/disability-inclusion.html. Accessed 31 October 2023.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Disability and health overview: impairments, activity limitations, and participation restrictions. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/ncbddd/disabilityandhealth/disability.html. Accessed 31 October 2023.
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). COVID-19. People with certain medical conditions. Available at: https://www.cdc.gov/coronavirus/2019-ncov/need-extra-precautions/people-.... Accessed 31 October 2023.

