A novel antibacterial approach of Cecropin-B peptide loaded on chitosan nanoparticles against MDR Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates
- PMID: 37966500
- PMCID: PMC10724327
- DOI: 10.1007/s00726-023-03356-4
A novel antibacterial approach of Cecropin-B peptide loaded on chitosan nanoparticles against MDR Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates
Abstract
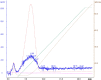
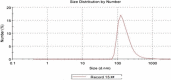
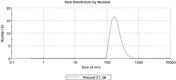
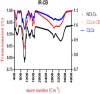
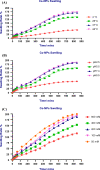
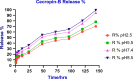
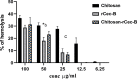
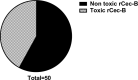
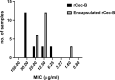
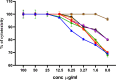
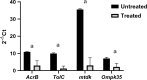
Egypt has witnessed the emergence of multidrug-resistant (MDR) Klebsiella pneumoniae, which has posed a serious healthcare challenge. The proper treatment choice for MDR-KP infections is not well determined which renders the problem more complicated, thus making the control of such infections a serious challenge for healthcare professionals. This study aims to encapsulate the cationic antimicrobial peptide; Cecropin-B (Cec-B), to increase its lifetime, drug targeting, and efficacy and study the antimicrobial effect of free and encapsulated recombinant rCec-B peptide on multidrug-resistant K. pneumoniae (MDR-KP) isolates. Fifty isolates were collected from different clinical departments at Theodore Bilharz Research Institute. Minimal inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of rCec-B against MDR-KP isolates were determined by the broth microdilution test. In addition, encapsulation of rCec-B peptide into chitosan nanoparticles and studying its bactericidal effect against MDR-KP isolates were also performed. The relative expression of efflux pump and porin coding genes (ArcrB, TolC, mtdK, and Ompk35) was detected by quantitative PCR in treated MDR-KP bacterial isolates compared to untreated isolates. Out of 60 clinical MDR isolates, 50 were MDR-KP. 60% of the isolates were XDR while 40% were MDR. rCec-B were bactericidal on 21 isolates, then these isolates were subjected to treatment using free nanocapsule in addition to the encapsulated peptide. Free capsules showed a mild cytotoxic effect on MDR-KP at the highest concentration. MIC of encapsulated rCec-B was higher than the free peptide. The expression level of genes encoding efflux and porin (ArcrB, TolC, mtdK, and Ompk35) was downregulated after treatment with encapsulated rCec-B. These findings indicate that encapsulated rCec-B is a promising candidate with potent antibacterial activities against drug-resistant K. pneumoniae.
Keywords: Antibacterial; Bactericidal; Cationic antimicrobial peptide; Cecropin; Chitosan; Egypt; Klebsiella pneumoniae; Multidrug-resistant; Nanocapsule; PCR.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that they have no competing interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Novel Cecropin D-Derived Short Cationic Antimicrobial Peptide Exhibits Antibacterial Activity Against Wild-Type and Multidrug-Resistant Strains of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Pseudomonas aeruginosa.Evol Bioinform Online. 2020 Jun 26;16:1176934320936266. doi: 10.1177/1176934320936266. eCollection 2020. Evol Bioinform Online. 2020. PMID: 32636607 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of OmpK35, OmpK36 Porins, and Production of β-Lactamases on Imipenem Susceptibility in Klebsiella pneumoniae Clinical Isolates, Cairo, Egypt.Microb Drug Resist. 2015 Dec;21(6):577-80. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2014.0226. Epub 2015 May 6. Microb Drug Resist. 2015. PMID: 25945596
-
In vivo selection of OmpK35-deficient mutant after cefuroxime therapy for primary liver abscess caused by Klebsiella pneumoniae.J Antimicrob Chemother. 2006 Oct;58(4):857-60. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkl308. Epub 2006 Jul 30. J Antimicrob Chemother. 2006. PMID: 16880175
-
Effect of Porins and blaKPC Expression on Activity of Imipenem with Relebactam in Klebsiella pneumoniae: Can Antibiotic Combinations Overcome Resistance?Microb Drug Resist. 2018 Sep;24(7):877-881. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2018.0065. Epub 2018 May 21. Microb Drug Resist. 2018. PMID: 29782237
-
Multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae: challenges for treatment, prevention and infection control.Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2018 Oct;16(10):749-761. doi: 10.1080/14787210.2018.1522249. Epub 2018 Sep 19. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther. 2018. PMID: 30207815 Review.
Cited by
-
GC-MS analysis, anti-inflammatory and anti-proliferative properties of the aerial parts of three Mesembryanthemum spp.Toxicol Rep. 2024 Nov 28;13:101829. doi: 10.1016/j.toxrep.2024.101829. eCollection 2024 Dec. Toxicol Rep. 2024. PMID: 39735355 Free PMC article.
-
Polysaccharide-Based Nanocarriers for Natural Antimicrobials: A Review.Polymers (Basel). 2025 Jun 24;17(13):1750. doi: 10.3390/polym17131750. Polymers (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40647761 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research Progress on Extracellular Matrix-Based Composite Materials in Antibacterial Field.Biomater Res. 2025 Jan 16;29:0128. doi: 10.34133/bmr.0128. eCollection 2025. Biomater Res. 2025. PMID: 39822928 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence and characterization of ESBL-producing diarrheagenic Escherichia coli from the poultry industry in Shanghai, China.Front Microbiol. 2025 Jun 30;16:1573614. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2025.1573614. eCollection 2025. Front Microbiol. 2025. PMID: 40661980 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aamir R, Ateya R, Arafa M, Yahia S. Ceftazidime/Avibactam efficiency tested In Vitro against Carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolated from Neonates with Sepsis. Microbes Infect Dis. 2021 doi: 10.21608/mid.2021.70493.1139. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

