Keratinocyte FABP5-VCP complex mediates recruitment of neutrophils in psoriasis
- PMID: 37967009
- PMCID: PMC10729729
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113449
Keratinocyte FABP5-VCP complex mediates recruitment of neutrophils in psoriasis
Abstract
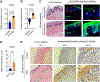
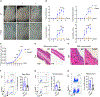
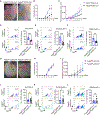
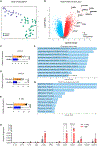
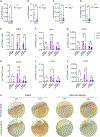
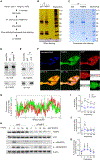
One of the hallmarks of intractable psoriasis is neutrophil infiltration in skin lesions. However, detailed molecular mechanisms of neutrophil chemotaxis and activation remain unclear. Here, we demonstrate a significant upregulation of epidermal fatty acid binding protein (E-FABP, FABP5) in the skin of human psoriasis and psoriatic mouse models. Genetic deletion of FABP5 in mice by global knockout and keratinocyte conditional (Krt6a-Cre) knockout, but not myeloid cell conditional (LysM-Cre) knockout, attenuates psoriatic symptoms. Immunophenotypic analysis shows that FABP5 deficiency specifically reduces skin recruitment of Ly6G+ neutrophils. Mechanistically, activated keratinocytes produce chemokines and cytokines that trigger neutrophil chemotaxis and activation in an FABP5-dependent manner. Proteomic analysis further identifies that FABP5 interacts with valosin-containing protein (VCP), a key player in NF-κB signaling activation. Silencing of FABP5, VCP, or both inhibits NF-κB/neutrophil chemotaxis signaling. Collectively, these data demonstrate dysregulated FABP5 as a molecular mechanism promoting NF-κB signaling and neutrophil infiltration in psoriasis pathogenesis.
Keywords: CP: Immunology; FABP5; NF-κB signaling; chemotaxis; chronic inflammation; epidermal fatty acid binding protein; keratinocytes; macrophages; neutrophil; psoriasis; valosin-containing protein.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Griffiths CE, and Barker JN (2007). Pathogenesis and clinical features of psoriasis. Lancet 370, 263–271. - PubMed
-
- van der Fits L, Mourits S, Voerman JSA, Kant M, Boon L, Laman JD, Cornelissen F, Mus AM, Florencia E, Prens EP, and Lubberts E (2009). Imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice is mediated via the IL-23/IL-17 axis. J. Immunol. 182, 5836–5845. - PubMed
-
- Machado Á, and Torres T (2018). Guselkumab for the Treatment of Psoriasis. BioDrugs 32, 119–128. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

