Randomised controlled trial to compare efficacy of standard care alone and in combination with homoeopathic treatment of moderate/severe COVID-19 cases
- PMID: 37967089
- PMCID: PMC10650991
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0292783
Randomised controlled trial to compare efficacy of standard care alone and in combination with homoeopathic treatment of moderate/severe COVID-19 cases
Abstract
Background & objectives: No definite treatment is known for COVID-19 till date. The objective of this study is to assess the efficacy of customized Homoeopathic medicines, when used as an add-on treatment to Standard of Care (SOC), in patients suffering from moderate to severe COVID-19 infection.
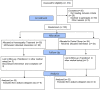
Methods: This was a randomized, controlled, single-blind, parallel-group trial where 214 COVID19-positive patients were screened for moderate and severe cases of COVID-19. Adjuvant homoeopathic medicines were given in the treatment group and SOC was given to both groups. The duration of oxygen support was compared as the primary outcome. Subjects were followed for 28 days or till the end-point of mechanical ventilation/ death.
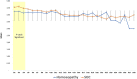
Results: Of 129 subjects included, 57 and 55 were severe; and 8 and 9 were moderate cases in Homoeopathy and SOC arms, respectively. In all, 9 (15.2%) participants in Homoeopathy and 20 (32.2%) participants in SOC arms eventually expired (p<0.05). Oxygen support was required for 9.84±7.00 and 14.92±7.549 days in Homoeopathy and SOC arms, respectively (p<0.005). Subjects receiving Homoeopathy (12.9±6.days) had a shorter hospitalization stay than in SOC (14.9±7.5 days). Homoeopathy arm (10.6±5.7 days) also showed statistically significant mean conversion time of of Realtime-Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR) from positive to negative than the SOC arm (12.9±5.6 days). The mean score of Clinical Outcome Ordinal Scale (COOS) was lower in the Homoeopathy arm. Laboratory markers [Interleukins (IL)-6, C-reactive protein (CRP), Neutrophils-Lymphocytes ratio (NLR)]were normalized earlier in Homoeopathy arm.
Conclusion: Homoeopathy, as add-on therapy with SOC for COVID-19 management, demonstrates a reduction in mortality and morbidity, by reduced requirement of oxygen and hospitalization. Some laboratory markers are normalized at an earlier time. Hence, there is overall control over the disease. Registry: The study was registered on the http://ctri.nic.in/Clinicaltrials website under identifier number: CTRI/2020/12/029668 on 9th December 2020.
Copyright: © 2023 Kaur et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous