Immunogenicity and Vaccine Shedding After 1 or 2 Doses of rVSVΔG-ZEBOV-GP Ebola Vaccine (ERVEBO®): Results From a Phase 2, Randomized, Placebo-controlled Trial in Children and Adults
- PMID: 37967326
- PMCID: PMC11006114
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciad693
Immunogenicity and Vaccine Shedding After 1 or 2 Doses of rVSVΔG-ZEBOV-GP Ebola Vaccine (ERVEBO®): Results From a Phase 2, Randomized, Placebo-controlled Trial in Children and Adults
Abstract
Background: The rVSVΔG-ZEBOV-GP vaccine (ERVEBO®) is a single-dose, live-attenuated, recombinant vesicular stomatitis virus vaccine indicated for the prevention of Ebola virus disease (EVD) caused by Zaire ebolavirus in individuals 12 months of age and older.
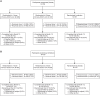
Methods: The Partnership for Research on Ebola VACcination (PREVAC) is a multicenter, phase 2, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of 3 vaccine strategies in healthy children (ages 1-17) and adults, with projected 5 years of follow-up (NCT02876328). Using validated assays (GP-ELISA and PRNT), we measured antibody responses after 1-dose rVSVΔG-ZEBOV-GP, 2-dose rVSVΔG-ZEBOV-GP (given on Day 0 and Day 56), or placebo. Furthermore, we quantified vaccine virus shedding in a subset of children's saliva using RT-PCR.
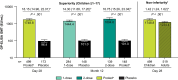
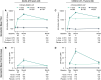
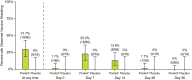
Results: In total, 819 children and 783 adults were randomized to receive rVSVΔG-ZEBOV-GP (1 or 2 doses) or placebo. A single dose of rVSVΔG-ZEBOV-GP increased antibody responses by Day 28 that were sustained through Month 12. A second dose of rVSVΔG-ZEBOV-GP given on Day 56 transiently boosted antibody concentrations. In vaccinated children, GP-ELISA titers were superior to placebo and non-inferior to vaccinated adults. Vaccine virus shedding was observed in 31.7% of children, peaking by Day 7, with no shedding observed after Day 28 post-dose 1 or any time post-dose 2.
Conclusions: A single dose of rVSVΔG-ZEBOV-GP induced robust antibody responses in children that was non-inferior to the responses induced in vaccinated adults. Vaccine virus shedding in children was time-limited and only observed after the first dose. Overall, these data support the use of rVSVΔG-ZEBOV-GP for the prevention of EVD in at-risk children. Clinical Trials Registration. The study is registered at ClinicalTrials.gov (NCT02876328), the Pan African Clinical Trials Registry (PACTR201712002760250), and the European Clinical Trials Register (EudraCT number: 2017-001798-18).
Keywords: Ebola; immunogenicity; pediatrics; vaccine; vaccine shedding.
© The Author(s) 2023. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Conflict of interest statement
Potential conflicts of interest. K. L., M. T. O., L. C., S. D., S. V., A. O., C. W., D .H., S. N., and B.-A. C. G. are employees of Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC, a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ USA, who may own stock and/or hold stock options in Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA. A. W. L., J. K. S., J. D., and A. M. were employees of Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC, a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA and may own/have owned stock and/or hold/held stock options in Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA at the time the study was conducted. E. L., B. H., and C. R. report provision of vaccines from Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC, a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA to the academic sponsors for the PREVAC trial, but no funding directly to themselves or their institution. J. M. reports provision of sample collection kits for the study sites, provision and support of lab software, technical support and supervision of lab activities, and lab data management. S. O. S. reports payments from Leidos to his institution. P. A. reports support for attending meetings and/or travel including Air tickets and accommodations for attending study related meetings during the conduct of the study. D. W.-J reports funding from Innovative Medicines Initiative 2 Joint Undertaking, additionally D. W.-J. reports funding and donations of an HPV vaccine (Gardasil®) from Merck Sharp & Dohme LLC, a subsidiary of Merck & Co., Inc., Rahway, NJ, USA for another unrelated study. All other authors report no potential conflicts. All authors have submitted the ICMJE Form for Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest. Conflicts that the editors consider relevant to the content of the manuscript have been disclosed.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization . Ebola virus disease. Available at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/ebola-virus-disease. Accessed 26 August 2022.
-
- Huber C, Finelli L, Stevens W. The economic and social burden of the 2014 Ebola outbreak in West Africa. J Infect Dis 2018; 218(suppl_5):S698–704. - PubMed
-
- Ebola in DRC: recommendations for accelerating outbreak control. WHO Scientific and Technical Advisory Group for Infectious Hazards (STAG-IH). 2019.

