Relationship between the cumulative exposure to atherogenic index of plasma and ischemic stroke: a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 37968612
- PMCID: PMC10652447
- DOI: 10.1186/s12933-023-02044-7
Relationship between the cumulative exposure to atherogenic index of plasma and ischemic stroke: a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: Atherogenic index of plasma (AIP) has been demonstrated as a surrogate marker for ischemic stroke, but there is limited evidence for the effect of long-term elevation of AIP on ischemic stroke. Therefore, we aimed to characterize the relationship between cumulative exposure to AIP and the risk of ischemic stroke.
Methods: A total of 54,123 participants in the Kailuan Study who attended consecutive health examinations in 2006, 2008, and 2010 and had no history of ischemic stroke or cancer were included. The time-weighted cumulative AIP (cumAIP) was calculated as a weighted sum of the mean AIP values for each time interval and then normalized to the total duration of exposure (2006-2010). Participants were divided into four groups according to quartile of cumAIP: the Q1 group, ≤-0.50; Q2 group, - 0.50 to - 0.12; Q3 group, - 0.12 to 0.28; and Q4 group, ≥ 0.28. Cox proportional hazard models were used to evaluate the relationship between cumAIP and ischemic stroke by calculating hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs).
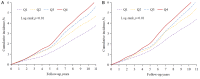
Results: After a median follow-up of 11.03 years, a total of 2,742 new ischemic stroke events occurred. The risk of ischemic stroke increased with increasing quartile of cumAIP. After adjustment for potential confounders, Cox regression models showed that participants in the Q2, Q3, and Q4 groups had significantly higher risks of ischemic stroke than those in the Q1 group. The HRs (95% CIs) for ischemic stroke in the Q2, Q3, and Q4 groups were 1.17 (1.03, 1.32), 1.33 (1.18, 1.50), and 1.45 (1.28, 1.64), respectively. The longer duration of high AIP exposure was significantly associated with increased ischemic stroke risk.
Conclusions: High cumulative AIP is associated with a higher risk of ischemic stroke, which implies that the long-term monitoring and maintenance of an appropriate AIP may help prevent such events.
Keywords: Atherogenic index of plasma; Cumulative exposure; Ischemic Stroke.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Relationship of cumulative exposure to the triglyceride-glucose index with ischemic stroke: a 9-year prospective study in the Kailuan cohort.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022 May 3;21(1):66. doi: 10.1186/s12933-022-01510-y. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2022. PMID: 35505313 Free PMC article.
-
Exposure of cumulative atherogenic index of plasma and the development of prediabetes in middle-aged and elderly individuals: evidence from the CHARLS cohort study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024 Sep 30;23(1):355. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02449-y. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 39350154 Free PMC article.
-
Association between atherogenic index of plasma and new-onset stroke in individuals with different glucose metabolism status: insights from CHARLS.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024 Jun 21;23(1):215. doi: 10.1186/s12933-024-02314-y. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 38907337 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal relationship between atherogenic dyslipidemia and inflammation and their joint cumulative effect on type 2 diabetes onset: a longitudinal cohort study.BMC Med. 2023 Jan 24;21(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s12916-023-02729-6. BMC Med. 2023. PMID: 36691001 Free PMC article.
-
Non-traditional lipid parameters as potential predictors of carotid plaque vulnerability and stenosis in patients with acute ischemic stroke.Neurol Sci. 2023 Mar;44(3):835-843. doi: 10.1007/s10072-022-06472-3. Epub 2022 Oct 27. Neurol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36301362 Review.
Cited by
-
Association between plain ropivacaine dose and spinal hypotension for cesarean delivery: a retrospective study.PeerJ. 2024 Oct 23;12:e18398. doi: 10.7717/peerj.18398. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39465154 Free PMC article.
-
Relationship between atherogenic index of plasma and length of stay in critically ill patients with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: a retrospective cohort study and predictive modeling based on machine learning.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025 Feb 28;24(1):95. doi: 10.1186/s12933-025-02654-3. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2025. PMID: 40022165 Free PMC article.
-
Association between malnutrition exposure in early life and elevated atherogenic index of plasma in adulthood.Front Nutr. 2025 May 20;12:1542731. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2025.1542731. eCollection 2025. Front Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40463473 Free PMC article.
-
Association between fasting glucose/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and cardiovascular disease risk in Chinese middle-aged and older adults: a longitudinal study.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025 Jul 14;12:1609891. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2025.1609891. eCollection 2025. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2025. PMID: 40727574 Free PMC article.
-
Association between long-term atherogenic index of plasma and carotid atherosclerosis: a prospective cohort study of a health examination population.BMJ Open. 2025 Jul 30;15(7):e098874. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2025-098874. BMJ Open. 2025. PMID: 40738628 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous