Population pharmacokinetic and exposure-response analyses of pemigatinib in patients with advanced solid tumors including cholangiocarcinoma
- PMID: 37969064
- PMCID: PMC10681497
- DOI: 10.1002/psp4.13064
Population pharmacokinetic and exposure-response analyses of pemigatinib in patients with advanced solid tumors including cholangiocarcinoma
Abstract
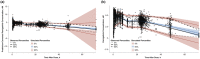
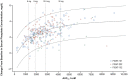
Pemigatinib is a selective, potent, oral inhibitor of fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR)1-3 with efficacy in patients with previously treated, advanced/metastatic cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) with FGFR2 alterations. A previously developed population pharmacokinetic (PK) model of pemigatinib was refined using an updated dataset with 467 participants from seven clinical studies, including patients with CCA. Updated PK model parameters were used to evaluate the association between pemigatinib exposure and efficacy and safety. Pemigatinib PK was adequately described by a two-compartment model with linear elimination and sequential zero- and first-order absorption. The final model successfully minimized, had a successful covariance step, and showed unbiased goodness-of-fit. Estimated first-order absorption rate constant and apparent clearance were 3.7/h and 10.7 L/h, respectively. Sex, baseline body weight, and concomitant use of phosphate binders, proton pump inhibitors, or histamine-2 antagonists significantly impacted PK parameters; however, the impact of covariates on PK exposure was not clinically significant. Steady-state pemigatinib exposure and mean change from baseline in serum phosphate concentration were associated with objective response rate in a bell-shaped relationship and were significantly associated with increased hyperphosphatemia. Pemigatinib exposure was associated with treatment-emergent adverse events, such as decreased appetite, nausea, and stomatitis, although the relationships were shallow. Overall, analyses indicate that 13.5 mg pemigatinib once daily in 21-day cycles (2 weeks on, 1 week off) offers a favorable benefit-risk profile in patients with advanced/metastatic or surgically unresectable CCA and is the optimal dose for clinical development.
© 2023 Incyte Corporation. CPT: Pharmacometrics & Systems Pharmacology published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
X.G., X.L., and X.C. are employees and shareholders of Incyte. A.A., A.N., and M.L. are employees of Certara. T.J. was an employee of Incyte at the time of the study and a current employee of Allorion Therapeutics.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

