Modified albumin-bilirubin predicted survival of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with immunotherapy
- PMID: 37969413
- PMCID: PMC10631433
- DOI: 10.4251/wjgo.v15.i10.1771
Modified albumin-bilirubin predicted survival of unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma patients treated with immunotherapy
Abstract
Background: Modified albumin-bilirubin (mALBI) grade has been established as a survival determinant in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients who receive locoregional and targeted therapies.
Aim: To investigate whether mALBI could predict survival in unresectable HCC (uHCC) patients who were treated with atezolizumab plus bevacizumab (AB).
Methods: A single-center, retrospective cohort study enrolled uHCC patients who received AB treatment between September 2020 and April 2023 and were followed up until June 2023. An association between mALBI and patient survival was determined using Cox proportional hazards analysis.
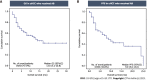
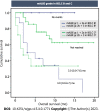
Results: Of the 83 patients, 67 patients (80.7%) were male with the mean age of 60.6 years. Among them, 22 patients (26.5%) were classified as Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer B, and 61 patients (73.5%) were classified as Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer C. Cirrhosis was present in 76 patients (91.6%), with 58 patients classified as Child-Turcotte-Pugh (CTP) A and 18 as CTP B. The median overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival were 13.0 mo [95% confidence interval (CI): 5.2-20.8] and 9.0 mo (95%CI: 5.0-13.0), respectively. The patients were divided into two groups based on mALBI grades: 42 patients (50.6%) in the mALBI 1 + 2a group; and 41 patients (49.4%) in the mALBI 2b + 3 group. During the median follow-up period of 7.0 mo, the mALBI 1 + 2a group exhibited significantly better survival compared to the mALBI 2b + 3 group, with a median OS that was not reached vs 3.0 mo (95%CI: 0.1-6.0, P < 0.001). In a subgroup of patients with CTP A, the mALBI 1 + 2a group also showed significantly longer survival compared to the mALBI 2b + 3 group, with a median OS that was not reached vs 6.0 mo (95%CI: 3.4-8.6, P < 0.001). In the multivariate analysis, both CTP class and mALBI grade were independently associated with survival, with adjusted hazard ratios (95%CI) of 2.63 (1.19-5.78, P = 0.020) and 3.90 (1.71-8.90, P = 0.001), respectively.
Conclusion: mALBI grades can determine survival of uHCC patients receiving AB treatment, particularly those who have mildly impaired liver function. This highlights the importance of assessing mALBI before initiating AB treatment to optimize therapeutic efficacy in clinical practice.
Keywords: Atezolizumab plus bevacizumab; Immunotherapy; Liver function; Modified albumin-bilirubin grade; Unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma.
©The Author(s) 2023. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Initial therapeutic results of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab for unresectable advanced hepatocellular carcinoma and the importance of hepatic functional reserve.Cancer Med. 2023 Feb;12(3):2646-2657. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5145. Epub 2022 Aug 14. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 35964253 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of the Albumin-Bilirubin Score for Predicting the Outcomes in Japanese Patients with Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma Treated with Ramucirumab: A Real-World Study.Oncology. 2021;99(4):203-214. doi: 10.1159/000511734. Epub 2020 Dec 4. Oncology. 2021. PMID: 33279908
-
Therapeutic efficacy of atezolizumab plus bevacizumab treatment for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with Child-Pugh class A or B liver function in real-world clinical practice.Hepatol Res. 2022 Sep;52(9):773-783. doi: 10.1111/hepr.13797. Epub 2022 Jun 11. Hepatol Res. 2022. PMID: 35633504
-
Impact of modified albumin-bilirubin grade on survival in patients with HCC who received lenvatinib.Sci Rep. 2021 Jul 14;11(1):14474. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-93794-5. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34262065 Free PMC article.
-
Modified Albumin-Bilirubin Model for Stratifying Survival in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Receiving Anticancer Therapy.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Oct 17;14(20):5083. doi: 10.3390/cancers14205083. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36291867 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The EZ-ALBI and PALBI scores contribute to the clinical application of ALBI in predicting postoperative recurrence of HCC.Sci Rep. 2025 Mar 17;15(1):9132. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-93716-9. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40097642 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-utility analysis of atezolizumab combined with bevacizumab for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma in Thailand.PLoS One. 2024 Mar 21;19(3):e0300327. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0300327. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38512900 Free PMC article.
-
The load of hepatitis B virus reduces the immune checkpoint inhibitors efficiency in hepatocellular carcinoma patients.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 27;15:1480520. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1480520. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39664382 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Forner A, Reig M, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2018;391:1301–1314. - PubMed
-
- Reig M, Forner A, Rimola J, Ferrer-Fàbrega J, Burrel M, Garcia-Criado Á, Kelley RK, Galle PR, Mazzaferro V, Salem R, Sangro B, Singal AG, Vogel A, Fuster J, Ayuso C, Bruix J. BCLC strategy for prognosis prediction and treatment recommendation: The 2022 update. J Hepatol. 2022;76:681–693. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Child CG, Turcotte JG. Surgery and portal hypertension. Major Probl Clin Surg. 1964;1:1–85. - PubMed
-
- Johnson PJ, Berhane S, Kagebayashi C, Satomura S, Teng M, Reeves HL, O'Beirne J, Fox R, Skowronska A, Palmer D, Yeo W, Mo F, Lai P, Iñarrairaegui M, Chan SL, Sangro B, Miksad R, Tada T, Kumada T, Toyoda H. Assessment of liver function in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma: a new evidence-based approach-the ALBI grade. J Clin Oncol. 2015;33:550–558. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

