Drug treatment service procurement: A systematic review of models, goals, and outcomes
- PMID: 37969897
- PMCID: PMC10634391
- DOI: 10.1177/14550725231157503
Drug treatment service procurement: A systematic review of models, goals, and outcomes
Abstract
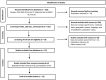
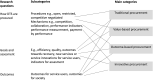
Aim: To explore the goals and outcomes of public procurement of drug treatment services in OECD countries. The study explores how these complex services are procured and delivered. Methods and data: A systematic review of the literature (1990-2020) identified four partly overlapping models of drug treatment service procurement that are here labelled traditional, value-based, outcome-based, and innovative. Results: Even though different forms of drug treatment services procurement are common, only 12 empirical studies that focused on procurement were found. The four models differ in their approaches to design and performance specifications and the role of competition and collaboration in the co-creation of value. Conclusions: Competition and incentives improve neither the efficiency nor the quality or the outcomes of complex drug treatment services. Whereas many studies focus on payment mechanisms, there are important research gaps that relate to the co-creation of value with and for the service-users and other stakeholders.
Keywords: co-creation; complexity; drug treatment services; public procurement; public value; systematic literature review.
© The Author(s) 2023.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Agger A., Lund D. (2017). Collaborative innovation in the public sector – new perspectives on the role of citizens? Scandinavian Journal of Public Administration, 21(3), 17–37.
-
- Barraket J., Keast R., Furneaux C. (2016). Social procurement and new public governance. Routledge.
-
- Crowley K., Head B. W. (2017). The enduring challenge of ‘wicked problems’: Revisiting rittel and webber. The enduring challenge of ‘wicked problems’: Revisiting Rittel and Webber. Policy Sciences, 50, 539–547. 10.1007/s11077-017-9302-4 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources