Seizure onset zone identification using phase-amplitude coupling and multiple machine learning approaches for interictal electrocorticogram
- PMID: 37969944
- PMCID: PMC10640557
- DOI: 10.1007/s11571-022-09915-x
Seizure onset zone identification using phase-amplitude coupling and multiple machine learning approaches for interictal electrocorticogram
Abstract
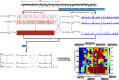
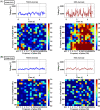
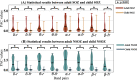
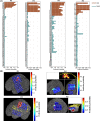
Automatic seizure onset zone (SOZ) localization using interictal electrocorticogram (ECoG) improves the diagnosis and treatment of patients with medically refractory epilepsy. This study aimed to investigate the characteristics of phase-amplitude coupling (PAC) extracted from interictal ECoG and the feasibility of PAC serving as a promising biomarker for SOZ identification. We employed the mean vector length modulation index approach on the 20-s ECoG window to calculate PAC features between low-frequency rhythms (0.5-24 Hz) and high frequency oscillations (HFOs) (80-560 Hz). We used statistical measures to test the significant difference in PAC between the SOZ and non-seizure onset zone (NSOZ). To overcome the drawback of handcraft feature engineering, we established novel machine learning models to learn automatically the characteristics of the obtained PAC features and classify them to identify the SOZ. Besides, to handle imbalanced dataset classification, we introduced novel feature-wise/class-wise re-weighting strategies in conjunction with classifiers. In addition, we proposed a time-series nest cross-validation to provide more accurate and unbiased evaluations for this model. Seven patients with focal cortical dysplasia were included in this study. The experiment results not only showed that a significant coupling at band pairs of slow waves and HFOs exists in the SOZ when compared with the NSOZ, but also indicated the effectiveness of the PAC features and the proposed models in achieving better classification performance .
Keywords: Electrocorticogram (ECoG); Focal cortical dysplasia (FCD); Interictal; Machine learning; Phase-amplitude coupling (PAC).
© The Author(s) 2022.
Figures



References
-
- Akter MS, Islam MR, Iimura Y, Sugano H, Fukumori K, Wang D, Tanaka T, Cichocki A. Multiband entropy-based feature-extraction method for automatic identification of epileptic focus based on high-frequency components in interictal ieeg. Sci Rep. 2020;10:7044. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-62967-z. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Akter MS, Islam MR, Tanaka T, Iimura Y, Mitsuhashi T, Sugano H, Wang D, Molla MKI. Statistical features in high-frequency bands of interictal ieeg work efficiently in identifying the seizure onset zone in patients with focal epilepsy. Entropy (Basel) 2020;22(12):1415. doi: 10.3390/e22121415. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

