Nephroprotective Efficacy of Echinops spinosus against a Glycerol-Induced Acute Kidney Injury Model
- PMID: 37969968
- PMCID: PMC10633848
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.3c06792
Nephroprotective Efficacy of Echinops spinosus against a Glycerol-Induced Acute Kidney Injury Model
Abstract
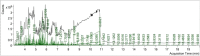
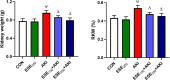
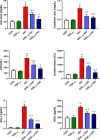
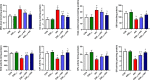
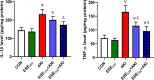
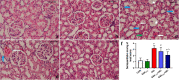
Nephroprotection or renal rescue is to revive and restore kidney function after damage, with no need for further dialysis. During acute kidney injury (AKI), sudden and recent reductions in kidney functions occur. Causes are multiple, and prompt intervention can be critical to diminish or prevent morbidity. Echinops spinosus (ES) is a curative plant with proven pharmacological and biological effects including anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antibacterial competencies. The principal goal of this research is to scrutinize the nephroprotective features of E. spinosa extract (ESE) against glycerol-induced AKI. Male Wistar albino rats were equally divided into five separated groups: negative control rats (vehicle-injected), ESE control rats (ESE-treated rats), positive control rats, glycerol-induced AKI-model rats (single IM injection of 50% glycerol), and 2 groups of diseased rats but pretreated with different concentrations of ESE for 7 days (ESE150 + AKI rats and ESE250 + AKI rats). Kidney tissues were collected and used for histopathology analysis. The relative kidney weight percentage was assessed. ESE effects were investigated via scanning several biomarkers, such as serum urea and creatinine, as kidney function biomarkers. Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and creatine kinase (CK) activities were examined as rhabdomyolysis (RM) indicators. Kidney injury molecule-1 (Kim-1) and neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (NGAL) were also examined to investigate kidney injury. Enzymatic and nonenzymatic oxidative stress markers were analyzed, namely, superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), glutathione reductase (GR), glutathione peroxidase (GPx), malondialdehyde (MDA), nitric oxide (NO), and reduced glutathione GSH. Proinflammatory cytokine [tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin-1 β (IL-1β)] and the renal proapoptotic protein (Bax) and antiapoptotic protein (Bcl-2) levels were evaluated. Statistical analysis for the resulting data revealed that ESE pretreatment turned AKI-induced biological antioxidant levels to an extent comparable to normal results. Furthermore, ESE decreased kidney function markers and RM-related biomarkers (LDH, CK, Kim-1, and NGAL) compared to those in untreated AKI-model rats. ESE treatment dropped the apoptotic renal Bax levels, enhanced antiapoptotic Bcl-2 manufacture, and disallowed the release of IL-1β and TNF-α. This study revealed the protective effect of ESE as therapeutic medicine against AKI-encouraged oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis. It can be effectively used as adjuvant therapy, helping in renal rescue, and for kidney healing in cases with risk factors of AKI.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Modulation of inflammatory, oxidative, and apoptotic stresses mediates the renoprotective effect of daidzein against glycerol-induced acute kidney injury in rats.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023 Dec;30(56):119016-119033. doi: 10.1007/s11356-023-30461-4. Epub 2023 Nov 3. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2023. PMID: 37919499
-
Using Green Biosynthesized Lycopene-Coated Selenium Nanoparticles to Rescue Renal Damage in Glycerol-Induced Acute Kidney Injury in Rats.Int J Nanomedicine. 2021 Jun 29;16:4335-4349. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S306186. eCollection 2021. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021. PMID: 34234429 Free PMC article.
-
Ameliorative effect of herbacetin against cyclophosphamide-induced nephrotoxicity in rats via attenuation of oxidative stress, inflammation, apoptosis and mitochondrial dysfunction.Hum Exp Toxicol. 2022 Jan-Dec;41:9603271221132140. doi: 10.1177/09603271221132140. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 36198566
-
Neutrophil gelatinase associated lipocalin as a biomarker for acute kidney injury in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting with cardiopulmonary bypass.Ann Vasc Surg. 2010 May;24(4):525-31. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2010.01.001. Epub 2010 Apr 2. Ann Vasc Surg. 2010. PMID: 20363104 Review.
-
Nephroprotective effects of substances of medicine food homology and traditional Chinese medicine phytochemicals against acute kidney injury.Front Pharmacol. 2025 Feb 19;16:1539886. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2025.1539886. eCollection 2025. Front Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40046749 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tumour-Derived, Extracellular Microvesicles in the Treatment of Acute Renal Failure: An Experimental Study.Med Sci (Basel). 2025 Apr 1;13(2):35. doi: 10.3390/medsci13020035. Med Sci (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40265382 Free PMC article.
-
Machine learning-based risk prediction of acute kidney disease and hospital mortality in older patients.Front Med (Lausanne). 2024 Aug 15;11:1407354. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2024.1407354. eCollection 2024. Front Med (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39211338 Free PMC article.
-
Terpenes in the management of chronic kidney disease.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Sep;397(9):6351-6368. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03098-4. Epub 2024 Apr 29. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38683370 Review.
References
-
- Bunel V.; Qu F.; Duez P.; Xu Q. Herbal Medicines for Acute Kidney Injury: Evidence, Gaps and Frontiers. World J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2015, 1, 47–66. 10.15806/j.issn.2311-8571.2015.0019. - DOI
-
- Zhang Y.; Xu Z.; He W.; Lin Z.; Liu Y.; Dai Y.; Chen W.; Chen W.; He W.; Duan C.; et al. Elevated Serum Uric Acid/Albumin Ratio as a Predictor of Post-Contrast Acute Kidney Injury After Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in Patients with ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction. J. Inflammation Res. 2022, 15, 5361–5371. 10.2147/JIR.S377767. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Prowle J. R.; Forni L. G.; Bell M.; Chew M. S.; Edwards M.; Grams M. E.; Grocott M. P. W.; Liu K. D.; McIlroy D.; Murray P. T.; et al. Postoperative acute kidney injury in adult non-cardiac surgery: joint consensus report of the Acute Disease Quality Initiative and PeriOperative Quality Initiative. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2021, 17 (9), 605–618. 10.1038/s41581-021-00418-2. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

