Highly Selective Colorimetric Sensor of Mercury(II) Ions by Andrographolide-Stabilized Silver Nanoparticles in Water and Antibacterial Evaluation
- PMID: 37970038
- PMCID: PMC10633854
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.3c03789
Highly Selective Colorimetric Sensor of Mercury(II) Ions by Andrographolide-Stabilized Silver Nanoparticles in Water and Antibacterial Evaluation
Abstract
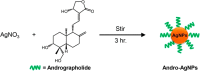
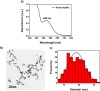
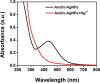
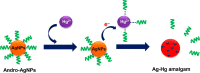
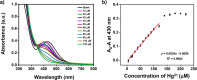
Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) are well known for their exceptional properties and versatility in various applications. This study used andrographolide as a biochemical stabilizer to synthesize AgNPs (andro-AgNPs). The andro-AgNPs were characterized by using UV-vis spectroscopy, revealing a surface plasmon resonance peak at 440 nm. Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy was also used to confirm the presence of AgNPs. Transmission electron microscopy was used to investigate the morphology of andro-AgNPs, which showed a spherical shape with an average diameter of 18.30 ± 5.57 nm (n = 205). Andro-AgNPs were utilized as a colorimetric sensor to detect mercury ions (Hg2+) in water, and the optimized detection conditions were evaluated using UV-vis spectroscopy with a linear range of 15-120 μM. The limit of detection and the limit of quantification for Hg2+ detection were found to be 11.15 and 37.15 μM, respectively. Furthermore, andro-AgNPs exhibited antibacterial properties against both Gram-positive (Staphylococcus aureus) and Gram-negative (Escherichia coli) bacteria. The results imply that andro-AgNPs hold promising potential for future biomedical applications.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A highly selective colorimetric sensor of mercury(ii) ions and hydrogen peroxide by biosynthesized silver nanoparticles in water and investigations of the interaction between silver and mercury.RSC Adv. 2025 Apr 2;15(13):10074-10084. doi: 10.1039/d5ra01733e. eCollection 2025 Mar 28. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40176822 Free PMC article.
-
Colorimetric detection of Hg(II) by γ-aminobutyric acid-silver nanoparticles in water and the assessment of antibacterial activities.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2021 Apr 15;251:119433. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2021.119433. Epub 2021 Jan 6. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2021. PMID: 33465574
-
Synthesis of hydroxyethylcellulose phthalate-modified silver nanoparticles and their multifunctional applications as an efficient antibacterial, photocatalytic and mercury-selective sensing agent.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Jan;256(Pt 1):128009. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.128009. Epub 2023 Nov 22. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 37995781
-
Pharmacological Effect of In Vitro Antioxidant Property and Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles (AgNPs) Utilizing Murraya koenigii Antibacterial Application.J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2024 Apr;16(Suppl 2):S1263-S1269. doi: 10.4103/jpbs.jpbs_567_23. Epub 2024 Apr 16. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2024. PMID: 38882802 Free PMC article.
-
Biogenic Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles using Lasiosiphon eriocephalus (Decne): In vitro Assessment of their Antioxidant, Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Activities.Pharm Nanotechnol. 2023;11(2):180-193. doi: 10.2174/2211738511666221207153116. Pharm Nanotechnol. 2023. PMID: 36503464
Cited by
-
A highly selective colorimetric sensor of mercury(ii) ions and hydrogen peroxide by biosynthesized silver nanoparticles in water and investigations of the interaction between silver and mercury.RSC Adv. 2025 Apr 2;15(13):10074-10084. doi: 10.1039/d5ra01733e. eCollection 2025 Mar 28. RSC Adv. 2025. PMID: 40176822 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Singh B. R.; Steinnes E.. Soil and Water Contamination by Heavy Metals. In Soil Processes Water Qual. CRC Press, 2020, 233−27110.1201/9781003070184-6 - DOI
-
- Wu Q.; Leung J. Y.; Geng X.; Chen S.; Huang X.; Li H.; Huang Z.; Zhu L.; Chen J.; Lu Y. Heavy Metal Contamination of Soil and Water in the Vicinity of an Abandoned E-Waste Recycling Site: Implications for Dissemination of Heavy Metals. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 506–507, 217–225. 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2014.10.121. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wan Z.; Duan L.; Hu X.; Li X.; Fang L.; Guo Q.; Sun D. Removal of Mercury from Flue Gas Using Coal Gasification Slag. Fuel Process. Technol. 2022, 231, 107258.10.1016/j.fuproc.2022.107258. - DOI
-
- Mitra S.; Chakraborty A. J.; Tareq A. M.; Emran T. B.; Nainu F.; Khusro A.; Idris A. M.; Khandaker M. U.; Osman H.; Alhumaydhi F. A.; et al. Impact of Heavy Metals on the Environment and Human Health: Novel Therapeutic Insights to Counter the Toxicity. J. King Saud Univ. Sci. 2022, 34, 101865.10.1016/j.jksus.2022.101865. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

