Multifaceted relationship between diabetes and kidney diseases: Beyond diabetes
- PMID: 37970131
- PMCID: PMC10642421
- DOI: 10.4239/wjd.v14.i10.1450
Multifaceted relationship between diabetes and kidney diseases: Beyond diabetes
Abstract
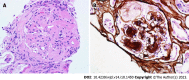
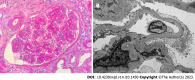
Diabetes mellitus is one of the most common causes of chronic kidney disease. Kidney involvement in patients with diabetes has a wide spectrum of clinical presentations ranging from asymptomatic to overt proteinuria and kidney failure. The development of kidney disease in diabetes is associated with structural changes in multiple kidney compartments, such as the vascular system and glomeruli. Glomerular alterations include thickening of the glomerular basement membrane, loss of podocytes, and segmental mesangiolysis, which may lead to microaneurysms and the development of pathognomonic Kimmelstiel-Wilson nodules. Beyond lesions directly related to diabetes, awareness of the possible coexistence of nondiabetic kidney disease in patients with diabetes is increasing. These nondiabetic lesions include focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, IgA nephropathy, and other primary or secondary renal disorders. Differential diagnosis of these conditions is crucial in guiding clinical management and therapeutic approaches. However, the relationship between diabetes and the kidney is bidirectional; thus, new-onset diabetes may also occur as a complication of the treatment in patients with renal diseases. Here, we review the complex and multifaceted correlation between diabetes and kidney diseases and discuss clinical presentation and course, differential diagnosis, and therapeutic oppor-tunities offered by novel drugs.
Keywords: Biomarkers; Diabetes; Diabetic kidney disease; Glomerular disease; Kidney biopsy; Nondiabetic kidney disease; Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors.
©The Author(s) 2023. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: Authors declare no conflict of interests for this article.
Figures
References
-
- Ritz E, Zeng XX, Rychlík I. Clinical manifestation and natural history of diabetic nephropathy. Contrib Nephrol. 2011;170:19–27. - PubMed
-
- Cho NH, Shaw JE, Karuranga S, Huang Y, da Rocha Fernandes JD, Ohlrogge AW, Malanda B. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2018;138:271–281. - PubMed
-
- Anders HJ, Huber TB, Isermann B, Schiffer M. CKD in diabetes: diabetic kidney disease versus nondiabetic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2018;14:361–377. - PubMed
-
- Pugliese G, Penno G, Natali A, Barutta F, Di Paolo S, Reboldi G, Gesualdo L, De Nicola L Italian Diabetes Society and the Italian Society of Nephrology. Diabetic kidney disease: new clinical and therapeutic issues. Joint position statement of the Italian Diabetes Society and the Italian Society of Nephrology on "The natural history of diabetic kidney disease and treatment of hyperglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes and impaired renal function". J Nephrol. 2020;33:9–35. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

