Prevalence of metabolic syndrome and chronic inflammation in psoriasis before and after biologic therapy: a prospective study
- PMID: 37970199
- PMCID: PMC10642736
- DOI: 10.15386/mpr-2631
Prevalence of metabolic syndrome and chronic inflammation in psoriasis before and after biologic therapy: a prospective study
Abstract
Background: As a chronic inflammatory disease, psoriasis affects not only the skin but also the metabolic profile of the patients. Biologic therapies, including tumor necrosis alpha (TNF-a) inhibitors and interleukin (IL)-12/23 and IL-17 antagonists, have proven effective in the reduction of psoriasis severity; however their impact on the metabolic and chronic inflammatory profiles of the patients remains incompletely elucidated.
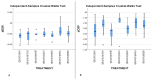
Methods: We performed a longitudinal case-control study on 106 psoriasis patients and an equal number of controls without the disease, as well as a prospective study on the patient group with the end point being 6 months of biologic therapy. Patients received either ixekizumab, secukinumab, guselkumab, certolizumab, ustekinumab, risankizumab, or adalimumab. Abdominal circumference, serum fasting glucose, triglycerides (TG), high-density lipoproteins (HDL), erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C reactive protein (CRP) were measured for both patients and controls, with an additional measurement for patients after 6 months.
Results: At baseline, the number of psoriasis patients suffering from obesity, metabolic syndrome, and chronic inflammation significantly outnumbered controls (p<0.05), with the calculated odds ratio being 1.88, 6.83, and 81.84 for these conditions in psoriasis, respectively. Biologic therapies increased the abdominal circumference of patients in a slight but significant fashion (p<0.05), as well as significantly improved HDL, CRP, ESR levels at 6 months (p<0.05). Moreover, after 6 months, the number of patients meeting the diagnostic criteria for metabolic syndrome and chronic inflammation was significantly lower than at baseline (p<0.001).
Conclusions: According to our results, biologic therapies improve the overall metabolic and inflammatory profiles of psoriasis patients, the most significant ameliorations being noticed for serum HDL, CRP, and ESR.
Keywords: abdominal circumference; chronic inflammation; diabetes; metabolic syndrome; obesity; psoriasis.
Figures
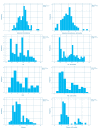
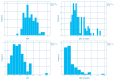
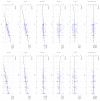
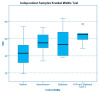
References
-
- Badri T, Kumar P, Oakley AM. StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; Aug 8, 2022. Plaque Psoriasis. - PubMed
-
- Swarup S, Goyal A, Grigorova Y, Zeltser R. StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; Oct 24, 2022. Metabolic Syndrome.
-
- Olufadi R, Byrne CD. Clinical and laboratory diagnosis of the metabolic syndrome. J Clin Pathol. 2008;61:697–706. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
