Common foods for boosting human immunity: A review
- PMID: 37970422
- PMCID: PMC10630845
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.3628
Common foods for boosting human immunity: A review
Abstract
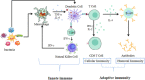
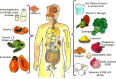
We are frequently exposed to potentially harmful microbes of various types on a daily basis. Our immune system is an amazing collection of unique organs and cells that defends us from hazardous germs as well as certain diseases. It plays a crucial role in protecting the body against external invaders, including bacteria, viruses, and parasites. Maintaining a healthy immune system requires consuming a balanced diet that provides a variety of macro- and micronutrients. By consuming sufficient amounts of water, minerals such as zinc and magnesium, micronutrients, herbs, and foods rich in vitamins C, D, and E, and adopting a healthy lifestyle, one can enhance their health and immunity, and prevent infections. This article provides a comprehensive review of the scientific literature on common foods known for their potential to boost human immunity. The review begins by discussing the various components of the immune system and their functions. It then delves into the current understanding of how nutrition can influence immune response, highlighting the importance of a well-balanced diet in supporting optimal immune function. The article presents an extensive analysis of a range of common foods that have been studied for their immune-boosting properties. These foods include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and animal-based foods. Each food category is explored in terms of its specific nutrients and bioactive compounds that contribute to immune support. Foods such as milk, eggs, fruits, leafy greens, and spices like onion, garlic, and turmeric contain beneficial compounds that can enhance the immune system's function, activate and inhibit immune cells, and interfere with multiple pathways that eventually lead to improved immune responses and defense. The available literature on the issue was accessed via online resources and evaluated thoroughly as a methodology for preparing this manuscript.
Keywords: common food; functional food; human health; immunity.
© 2023 The Authors. Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no financial or personal conflicts of interest that could influence the content or findings presented in this work. This includes but is not limited to any financial interests, affiliations, or involvements with organizations that may have a direct or indirect interest in the subject matter discussed in the manuscript.
Figures
References
-
- Ahmad, S. R. , & Ghosh, P. (2020). Probiotic potential of lactic acid to improve immunity during COVID‐19 pandemic (a mini review). Indian Journal of Pure & Applied Biosciences, 8(5), 66–72. 10.18782/2582-2845.8346 - DOI
-
- Albers, R. , Bourdet‐Sicard, R. , Braun, D. , Calder, P. C. , Herz, U. , Lambert, C. , Lenoir‐Wijnkoop, I. , Méheust, A. , Ouwehand, A. , Phothirath, P. , Sako, T. , Salminen, S. , Siemensma, A. , Van Loveren, H. , & Sack, U. (2013). Monitoring immune modulation by nutrition in the general population: Identifying and substantiating effects on human health. British Journal of Nutrition, 110(Suppl 2), S30. 10.1017/S0007114513001505 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arreola, R. , Quintero‐Fabián, S. , López‐Roa, R. , Flores‐Gutiérrez, E. , Reyes‐Grajeda, J. , Carrera‐Quintanar, L. , & Ortuño‐Sahagún, D. (2015). Immunomodulation and anti‐inflammatory effects of garlic compounds: Discovery service for Endeavour college of natural health library. Journal of Immunology Research, 2015, 1–13. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources