Performance evaluation of NeuMoDx 96 system for hepatitis B and C viral load
- PMID: 37970568
- PMCID: PMC10642378
- DOI: 10.5501/wjv.v12.i4.233
Performance evaluation of NeuMoDx 96 system for hepatitis B and C viral load
Abstract
Background: Hepatitis B virus (HBV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) viral load (VL) estimation is essential for the management of both HBV and HCV infections. Due to a longer turnaround time for VL estimation, many patients drop out from the cascade of care. To achieve the global goals of reducing morbidity and mortality due to HBV/HCV and moving towards their elimination by 2030, molecular diagnostic platforms with faster and random (i.e. single sample) access are needed.
Aim: To evaluate the performance of the recently launched NeuMoDx 96 random access system with the conventional COBAS®AmpliPrep/COBAS TaqMan system for HBV and HCV VL estimation.
Methods: Archived once-thawed plasma samples were retrieved and tested on both platforms. Correlation between the assays was determined by linear regression and Bland-Altman analysis. The study included samples from 186 patients, 99 for HBV of which 49 were true infected HBV cases (hepatitis B surface antigen, anti-hepatitis B core antibody, and HBV DNA-positive) and 87 for HCV assay in which 39 were true positives for HCV infection (anti-HCV and HCV RNA-positive).
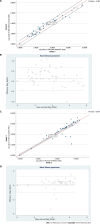
Results: The median VL detected by NeuMoDx for HBV was 2.9 (interquartile range [IQR]: 2.0-4.3) log10 IU/mL and by COBAS it was 3.70 (IQR: 2.28-4.56) log10 IU/mL, with excellent correlation (R2 = 0.98). In HCV, the median VL detected by NeuMoDx was 4.9 (IQR: 4.2-5.4) log10 IU/mL and by COBAS it was 5.10 (IQR: 4.07-5.80) log10 IU/mL with good correlation (R2 = 0.96).
Conclusion: The overall concordance between both the systems was 100% for both HBV and HCV VL estimation. Moreover, no genotype-specific bias for HBV/HCV VL quantification was seen in both the systems. Our findings reveal that NeuMoDx HBV and HCV quantitative assays have shown overall good clinical performance and provide faster results with 100% sensitivity and specificity compared to the COBAS AmpliPrep/COBAS TaqMan system.
Keywords: COBAS AmpliPrep; Hepatitis B; Hepatitis C; NeuMoDx; Random access; Viral load.
©The Author(s) 2023. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare having no conflict of interest that pertains to this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rapid, random-access, and quantification of hepatitis B virus using the Cepheid Xpert HBV viral load assay.J Med Virol. 2021 Jun;93(6):3999-4003. doi: 10.1002/jmv.26392. Epub 2020 Aug 25. J Med Virol. 2021. PMID: 32761911 Free PMC article.
-
Multicenter comparison of the new Cobas 6800 system with Cobas Ampliprep/Cobas TaqMan and Abbott RealTime for the quantification of HIV, HBV and HCV viral load.J Clin Virol. 2017 Nov;96:49-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2017.09.007. Epub 2017 Sep 20. J Clin Virol. 2017. PMID: 28950186
-
Verification of the Roche cobas® 6800 PCR 200 µl and 500 µl protocols for the quantification of HIV-1 RNA, HBV DNA and HCV RNA and evaluation with COBAS® Ampliprep/COBAS® TaqMan® assays.J Med Microbiol. 2018 Dec;67(12):1711-1717. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.000838. Epub 2018 Oct 16. J Med Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 30325300
-
Clinical performance of two new, fully integrated molecular platforms used for HIV-1, HBV and HCV viral load analysis, the NeuMoDx 288 and the Alinity m.J Clin Virol. 2023 Mar;160:105376. doi: 10.1016/j.jcv.2022.105376. Epub 2023 Jan 2. J Clin Virol. 2023. PMID: 36640531
-
Reflex Hepatitis C Virus Viral Load Testing Following an Initial Positive Hepatitis C Virus Antibody Test: A Global Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Clin Infect Dis. 2023 Oct 13;77(8):1137-1156. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciad126. Clin Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 37648655
Cited by
-
Newer Diagnostic Virological Markers for Hepatitis B Virus Infection.Euroasian J Hepatogastroenterol. 2024 Jul-Dec;14(2):214-220. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10018-1450. Epub 2024 Dec 27. Euroasian J Hepatogastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 39802850 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Global hepatitis report 2017. [cited 20 July 2023]. Available from: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241565455 .
-
- Chen CL, Yang JY, Lin SF, Sun CA, Bai CH, You SL, Chen CJ, Kao JH, Chen PJ, Chen DS. Slow decline of hepatitis B burden in general population: Results from a population-based survey and longitudinal follow-up study in Taiwan. J Hepatol . 2015;63:354–363. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization. Progress report on HIV, viral hepatitis and sexually transmitted infections 2019. [cited 20 July 2023]. Available from:https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/progress-report-on-hiv-viral-hep... .
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

