Viral and host factors drive a type 1 Epstein-Barr virus spontaneous lytic phenotype
- PMID: 37971257
- PMCID: PMC10746244
- DOI: 10.1128/mbio.02204-23
Viral and host factors drive a type 1 Epstein-Barr virus spontaneous lytic phenotype
Abstract
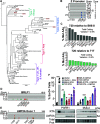
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infects over 95% of adults worldwide. Given its connection to various cancers and autoimmune disorders, it is important to understand the mechanisms by which infection with EBV can lead to these diseases. In this study, we describe an unusual spontaneous lytic phenotype in EBV strains isolated from Kenyan endemic Burkitt lymphoma patients. Because lytic replication of EBV has been linked to the pathogenesis of various diseases, these data could illuminate viral and host factors involved in this process.
Keywords: Epstein–Barr virus; burkitt lymphoma; herpesvirus; lytic replication.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
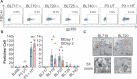
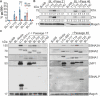
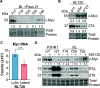
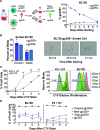



References
-
- Bristol JA, Djavadian R, Albright ER, Coleman CB, Ohashi M, Hayes M, Romero-Masters JC, Barlow EA, Farrell PJ, Rochford R, Kalejta RF, Johannsen EC, Kenney SC, Flemington EK. 2018. A cancer-associated Epstein-Barr virus BZLF1 promoter variant enhances lytic infection. PLoS Pathog 14:e1007179. doi:10.1371/journal.ppat.1007179 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
