Scientometric Analysis and Mapping of Scientific Articles on Multiple Sclerosis-Related Neurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction
- PMID: 37971389
- PMCID: PMC10765193
- DOI: 10.5152/tud.2023.23137
Scientometric Analysis and Mapping of Scientific Articles on Multiple Sclerosis-Related Neurogenic Lower Urinary Tract Dysfunction
Abstract
Objective: Patients suffering from multiple sclerosis (MS) frequently experience lower urinary tract (LUT) dysfunction, which significantly impacts their quality of life. This study's objective was to conduct a scientometric analysis of the literature on MS-induced neurogenic LUT dysfunction.
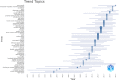
Methods: Using bibliometric methods, we examined the literature on neurogenic lower urinary tract dysfunction (NLUTD) in MS patients without restricting it to prevalence studies or specific management methods. We considered contributions from authors, organizations, nations/regions, as well as the evolution of theoretical frameworks, research subtopics, and influential papers. In January 2023, we searched the complete Scopus database, without imposing any language or date constraints, identifying relevant documents related to urology clinical investigations of MS-induced NLUTD. The original articles were categorized into 4 groups: narrative reviews, systematic reviews and meta-analyses, research of levels 1-4, and case reports/series.
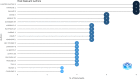
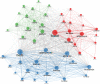
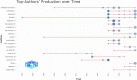
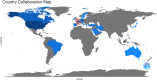
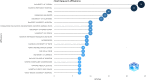
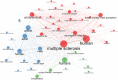
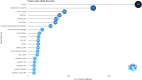
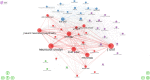
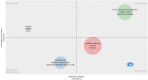
Results: On January 1, 2023, our search yielded 72 sources published between 1977 and 2022, including journals and books. The average time before publication was 11.2 years. Each document received an average of 18.1 citations, totaling 1.299 citations per year. The author's analysis explored relationships, productivity, and coauthorship networks among authors and institutions based on bibliographic records. Chartier-Kastler E, Karmonik C, and Khavari R ranked highest with 8 publications each. The University of Catania claimed the top position, followed by Houston Methodist Hospital and Paris University, recognized as the leading institutions in this field.
Conclusion: An analysis of diagnosis, therapy, and rehabilitation of MS-related NLUTD may be helpful for future bibliometric research in the field to better direct output.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
