Predictive value of serum creatinine and total bilirubin for long-term death in patients with ischemic heart disease: A cohort study
- PMID: 37971981
- PMCID: PMC10653523
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0294335
Predictive value of serum creatinine and total bilirubin for long-term death in patients with ischemic heart disease: A cohort study
Abstract
Background: Ischemic heart disease (IHD) has a high mortality in the population. Although serum creatinine (Cr) and serum total bilirubin (TBil) are rapid and readily available biomarkers in routine blood tests, there is a lack of literature on the prognostic value of combined Cr and TBil tests for IHD. This study aimed to evaluate a combined equation based on Cr and TBil to predict the long-term risk of death in IHD and to find indicators sensitive to the prognosis of IHD patients.
Method: In this study, 2625 patients with IHD were included, and the combined value and combined equations of Cr and TBil were obtained by logistic regression analysis based on Cr and TBil collected at the time of admission. Patients were divided into four groups according to the quartiles of the combined value. COX proportional hazard regression model was used to analyze the risk factors for long-term death in IHD patients. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were used to evaluate the prognostic effect of Cr, TBil and combined value on long-term death events.
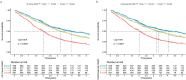
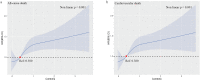
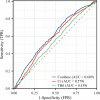
Results: Logistic regression analysis was performed for long-term death events with Cr and TBil as independent variables, and the logit regression model was Logit(P) = 0.0129×TBil+0.007×Cr-0.417. Multifactorial Cox regression analysis showed that high values of the equation were independent risk factors for long-term death events (all-cause death: HR 1.457, 95% CI 1.256-1.689, P<0.001; cardiovascular death: HR 1.452, 95% CI 1.244-1.695, P<0.001). Combined Cr and TBil value are more valuable in predicting long-term death (AUC: 0.609, 95% CI 0.587-0.630, P<0.001).
Conclusion: Combined Cr and TBil assay is superior to single biomarkers for predicting long-term death in patients with IHD. High values of the equation are independent predictors of long-term death and can be used to identify patients at high risk for IHD.
Copyright: © 2023 Seyiti et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Establishment and evaluation of early in-hospital death prediction model for patients with acute pancreatitis in intensive care unit].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2023 Aug;35(8):865-869. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20220713-00660. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2023. PMID: 37593868 Chinese.
-
Serum total bilirubin and long-term prognosis of patients with new-onset non-ST elevation myocardial infarction: a cohort study.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2022 Apr 12;22(1):165. doi: 10.1186/s12872-022-02607-8. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2022. PMID: 35413813 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation between serum bilirubin levels and the severity as well as the prognosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Chron Respir Dis. 2020 Jan-Dec;17:1479973120957676. doi: 10.1177/1479973120957676. Chron Respir Dis. 2020. PMID: 32909821 Free PMC article.
-
[Study on the application value of MELD-Na, CLIF-C OFs, COSSH-ACLFs and NLR scoring systems in patients with hepatitis B virus related acute-on-chronic liver failure].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020 Dec;32(12):1496-1501. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20200720-00536. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2020. PMID: 33541504 Chinese.
-
Five-year native liver survival analysis in biliary atresia from a single large Chinese center: The death/liver transplantation hazard change and the importance of rapid early clearance of jaundice.J Pediatr Surg. 2019 Aug;54(8):1680-1685. doi: 10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2018.09.025. Epub 2018 Oct 30. J Pediatr Surg. 2019. PMID: 30518490
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

