Extracellular vesicle-encapsulated microRNA-296-3p from cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes ovarian cancer development through regulation of the PTEN/AKT and SOCS6/STAT3 pathways
- PMID: 37972389
- PMCID: PMC10823290
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.16014
Extracellular vesicle-encapsulated microRNA-296-3p from cancer-associated fibroblasts promotes ovarian cancer development through regulation of the PTEN/AKT and SOCS6/STAT3 pathways
Abstract
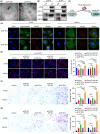
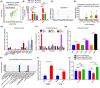
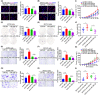
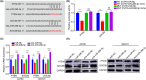
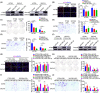
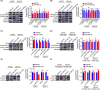
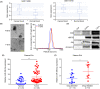
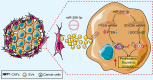
Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), as important components of the tumor microenvironment, can regulate intercellular communication and tumor development by secreting extracellular vesicles (EVs). However, the role of CAF-derived EVs in ovarian cancer has not been fully elucidated. Here, using an EV-microRNA sequencing analysis, we reveal specific overexpression of microRNA (miR)-296-3p in activated CAF-derived EVs, which can be transferred to tumor cells to regulate the malignant phenotypes of ovarian cancer cells. Moreover, overexpression of miR-296-3p significantly promotes the proliferation, migration, invasion, and drug resistance of ovarian cancer cells in vitro, as well as tumor growth in vivo, while its inhibition has the opposite effects. Further mechanistic studies reveal that miR-296-3p promotes ovarian cancer progression by directly targeting PTEN and SOCS6 and activating AKT and STAT3 signaling pathways. Importantly, increased expression of miR-296-3p encapsulated in plasma EVs is closely correlated with tumorigenesis and chemoresistance in patients with ovarian cancer. Our results highlight the cancer-promoting role of CAF-derived EVs carrying miR-296-3p in ovarian cancer progression for the first time, and suggest that miR-296-3p encapsulated in CAF-derived EVs could be a diagnostic biomarker and therapeutic target for ovarian cancer.
Keywords: cancer progression; cancer-associated fibroblast; extracellular vesicle; miR-296-3p; ovarian cancer.
© 2023 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ovarian tumor microenvironment contributes to tumor progression and chemoresistance.Cancer Drug Resist. 2024 Dec 17;7:53. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2024.111. eCollection 2024. Cancer Drug Resist. 2024. PMID: 39802952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FAPhigh α-SMAlow cancer-associated fibroblast-derived SLPI protein encapsulated in extracellular vesicles promotes ovarian cancer development via activation of PI3K/AKT and downstream signaling pathways.Mol Carcinog. 2022 Oct;61(10):910-923. doi: 10.1002/mc.23445. Epub 2022 Jul 8. Mol Carcinog. 2022. PMID: 35801406 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular vesicles derived from cancer-associated fibroblasts carry tumor-promotive microRNA-1228-3p to enhance the resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells to sorafenib.Hum Cell. 2023 Jan;36(1):296-311. doi: 10.1007/s13577-022-00800-7. Epub 2022 Nov 23. Hum Cell. 2023. PMID: 36424471
-
Elevating microRNA-1-3p shuttled by cancer-associated fibroblasts-derived extracellular vesicles suppresses breast cancer progression and metastasis by inhibiting GLIS1.Cancer Gene Ther. 2021 Jun;28(6):634-648. doi: 10.1038/s41417-020-00244-x. Epub 2020 Nov 5. Cancer Gene Ther. 2021. PMID: 33154575
-
Cancer-associated fibroblast-derived extracellular vesicles: regulators and therapeutic targets in the tumor microenvironment.Cancer Drug Resist. 2025 Jan 7;8:2. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2024.152. eCollection 2025. Cancer Drug Resist. 2025. PMID: 39935427 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Upregulation of miRNA-450b-5p targets ACTB to affect drug resistance and prognosis of ovarian cancer via the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.Transl Cancer Res. 2024 Sep 30;13(9):4800-4812. doi: 10.21037/tcr-24-292. Epub 2024 Sep 27. Transl Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39430863 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in small extracellular vesicles: roles in the tumor microenvironment and epithelial ovarian cancer diagnosis and treatment.Front Oncol. 2025 Feb 11;15:1526944. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2025.1526944. eCollection 2025. Front Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40008006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemoresistance and the tumor microenvironment: the critical role of cell-cell communication.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Oct 10;22(1):486. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01857-7. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39390572 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic interactions in the tumor niche: how the cross-talk between CAFs and the tumor microenvironment impacts resistance to therapy.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Feb 22;11:1343523. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1343523. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38455762 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ovarian tumor microenvironment contributes to tumor progression and chemoresistance.Cancer Drug Resist. 2024 Dec 17;7:53. doi: 10.20517/cdr.2024.111. eCollection 2024. Cancer Drug Resist. 2024. PMID: 39802952 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Stewart C, Ralyea C, Lockwood S. Ovarian cancer: An integrated review. Semin Oncol Nurs. 2019;35:151‐156. - PubMed
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, et al. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71:209‐249. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

