Specific intracellular retention of circSKA3 promotes colorectal cancer metastasis by attenuating ubiquitination and degradation of SLUG
- PMID: 37973787
- PMCID: PMC10654574
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-023-06279-w
Specific intracellular retention of circSKA3 promotes colorectal cancer metastasis by attenuating ubiquitination and degradation of SLUG
Abstract
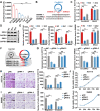
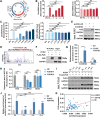
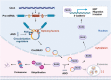
Our previous study demonstrated that tumor-suppressor circular RNAs (circRNAs) can be specifically secreted outside of colorectal cancer (CRC) cells within exosomes to maintain tumor cell fitness. However, whether tumor-driving circRNAs can be specifically retained in cells to facilitate tumor progression remains unknown. In this study, circRNA-seq showed that circSKA3 was significantly upregulated in CRC tissues but downregulated in serum samples from CRC patients. In addition, circSKA3 promoted CRC progression in vitro and in vivo and was retained in CRC cells via a specific cellmotif element. Interestingly, the cellmotif element was also the site of interaction of circSKA3 with SLUG, which inhibited SLUG ubiquitination degradation and promoted CRC epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Moreover, FUS was identified as a key circularization regulator of circSKA3 that bound to the key element. Finally, we designed and synthesized specific antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) targeting circularization and cellmotif elements, which repressed circSKA3 expression, abolished the SLUG-circSKA3 interaction, and further inhibited CRC EMT and metastasis in vitro and in vivo.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Sevoflurane suppresses colorectal cancer malignancy by modulating β-catenin ubiquitination degradation via circSKA3.Cell Signal. 2024 Feb;114:110987. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2023.110987. Epub 2023 Nov 27. Cell Signal. 2024. PMID: 38029946
-
circSKA3 promotes colorectal cancer metastases through miR-1238 and methylation.Mol Cell Biochem. 2024 Apr;479(4):941-950. doi: 10.1007/s11010-023-04773-5. Epub 2023 May 31. Mol Cell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 37256443 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor-suppressive circRHOBTB3 is excreted out of cells via exosome to sustain colorectal cancer cell fitness.Mol Cancer. 2022 Feb 11;21(1):46. doi: 10.1186/s12943-022-01511-1. Mol Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35148775 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive landscape and future perspectives of circular RNAs in colorectal cancer.Mol Cancer. 2021 Feb 3;20(1):26. doi: 10.1186/s12943-021-01318-6. Mol Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33536039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circular RNAs: The crucial regulatory molecules in colorectal cancer.Pathol Res Pract. 2020 Apr;216(4):152861. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2020.152861. Epub 2020 Feb 11. Pathol Res Pract. 2020. PMID: 32061452 Review.
Cited by
-
Circular RNA in cancer.Nat Rev Cancer. 2024 Sep;24(9):597-613. doi: 10.1038/s41568-024-00721-7. Epub 2024 Jul 29. Nat Rev Cancer. 2024. PMID: 39075222 Review.
-
The Role and Function of Non-Coding RNAs in Cholangiocarcinoma Invasiveness.Biomedicines. 2025 Jun 3;13(6):1369. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines13061369. Biomedicines. 2025. PMID: 40564088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overexpression of Circular PRMT1 Transcripts in Colorectal Adenocarcinoma Predicts Recurrence and Poor Overall Survival.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jul 11;26(14):6683. doi: 10.3390/ijms26146683. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40724932 Free PMC article.
-
Implications in Cancer of Nuclear Micro RNAs, Long Non-Coding RNAs, and Circular RNAs Bound by PRC2 and FUS.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Feb 21;16(5):868. doi: 10.3390/cancers16050868. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38473229 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Post-Translational Modifications in Multiple Myeloma: Mechanisms of Drug Resistance and Therapeutic Opportunities.Biomolecules. 2025 May 12;15(5):702. doi: 10.3390/biom15050702. Biomolecules. 2025. PMID: 40427595 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

