Rescue of murine hind limb ischemia via angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis promoted by cellular communication network factor 2
- PMID: 37973852
- PMCID: PMC10654495
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-47485-y
Rescue of murine hind limb ischemia via angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis promoted by cellular communication network factor 2
Abstract
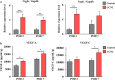
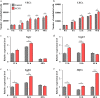
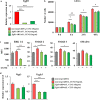
Critical limb ischemia (CLI) is caused by severe arterial blockage with reduction of blood flow. The aim of this study was to determine whether therapeutic angiogenesis using cellular communication network factor 2 (CCN2) would be useful for treating CLI in an animal model. Recombinant CCN2 was administered intramuscularly to male C57BL/6J mice with hind limb ischemia. The therapeutic effect was evaluated by monitoring blood flow in the ischemic hind limb. In an in vivo assay, CCN2 restored blood flow in the ischemic hind limb by promoting both angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. VEGF-A and VEGF-C expression levels increased in the ischemic limb after treatment with CCN2. In an in vitro assay, CCN2 promoted proliferation of vascular and lymphatic endothelial cells, and it upregulated expression of Tgfb1 followed by expression of Vegfc and Vegfr3 in lymphatic endothelial cells under hypoxia. Suppression of Tgfb1 did not affect the activity of CCN2, activation of the TGF-β/SMAD signaling pathway, or expression of Vegfr3 in lymphatic endothelial cells. In summary, treatment using recombinant CCN2 could be a promising therapeutic strategy for CLI.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor-C derived from CD11b+ cells induces therapeutic improvements in a murine model of hind limb ischemia.J Vasc Surg. 2013 Apr;57(4):1090-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jvs.2012.08.121. Epub 2012 Dec 7. J Vasc Surg. 2013. PMID: 23219511
-
No influence on tumor growth by intramuscular injection of adipose-derived regenerative cells: safety evaluation of therapeutic angiogenesis with cell therapy.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2021 Jan 1;320(1):H447-H457. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00564.2020. Epub 2020 Nov 13. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33185457
-
VEGF-C regulates lymphangiogenesis and capillary stability by regulation of PDGF-B.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2009 Nov;297(5):H1685-96. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00015.2009. Epub 2009 Sep 4. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19734356
-
Lymphangiogenesis and angiogenesis rescue murine ischemic hindlimb via transient receptor potential vanilloid 4.J Pharmacol Sci. 2021 Aug;146(4):244-248. doi: 10.1016/j.jphs.2021.04.009. Epub 2021 May 11. J Pharmacol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34116738 Review.
-
Systematic Interrogation of Angiogenesis in the Ischemic Mouse Hind Limb: Vulnerabilities and Quality Assurance.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020 Oct;40(10):2454-2467. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.315028. Epub 2020 Aug 13. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020. PMID: 32787524 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of Neonatal Porcine Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cell Xenotransplantation for the Therapy of Hind Limb Lymphedema in Mice.Cell Transplant. 2024 Jan-Dec;33:9636897241260195. doi: 10.1177/09636897241260195. Cell Transplant. 2024. PMID: 38867486 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baubeta Fridh E, Andersson M, Thuresson M, Sigvant B, Kragsterman B, Johansson S, et al. Amputation rates, mortality, and pre-operative comorbidities in patients revascularised for intermittent claudication or critical limb ischaemia: A population based study. Eur. J. Vasc. Endovasc. Surg. 2017;54(4):480–486. doi: 10.1016/j.ejvs.2017.07.005. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

